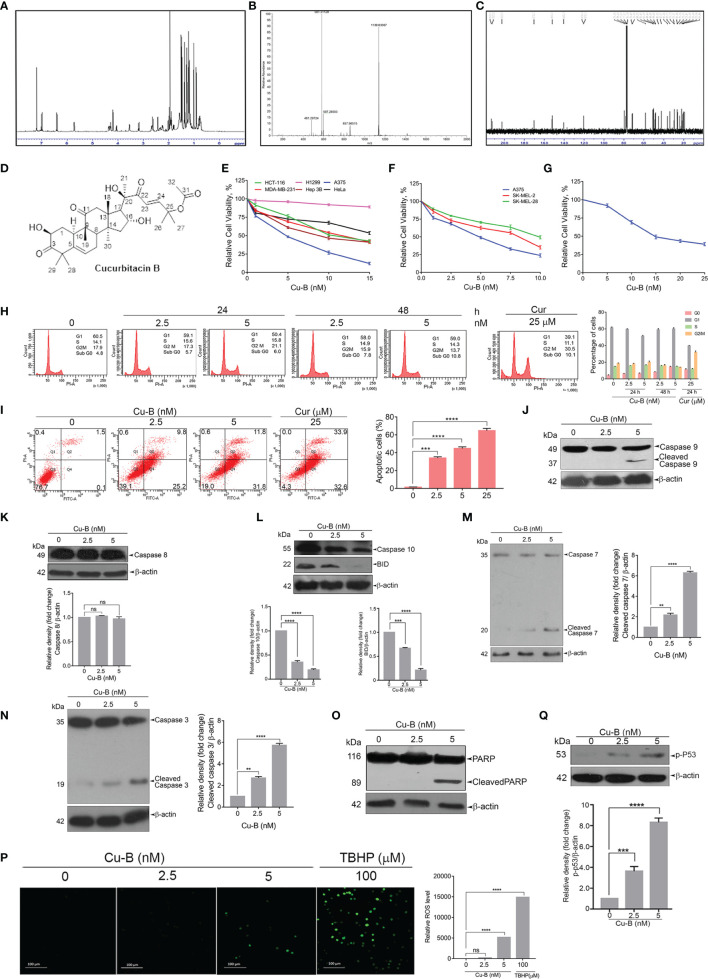
Figure 3.
Purification and structural elucidation of Cu-B from ECF fraction of C. epigaeus rhizome (A–D) 1H NMR, HR-ESI-MS, 13C NMR data, and structure of C. epigaeus-derived Cu-B. (E–G) Cytotoxicity assessment of Cu-B in melanoma cell lines and normal fibroblast cells (H) Cu-B does not affect any phases of the cell cycle in A375 cells as demonstrated by flow cytometry. (I) The extent of apoptosis induced by Cu-B was quantitated by Annexin V/PI FACS analysis (J–O) Cu-B treatment induces activation of caspases and cleavage of PARP in A375 cells as analyzed by immunoblotting. Cu-B promotes the cleavages of caspase-10 and Bid as analyzed by immunoblotting. (P) ROS production in response to Cu-B treatment in A375 cells as detected by fluorescence microscopy. (Q) Cu-B potentiates p53 activation in A375 cells as analyzed by immunoblotting. Data are representative of three independent experiments (Mean±SEM) and P-values are calculated using one-way ANOVA. ****P ≤0.0001, ***P ≤0.001, **P ≤0.01 and ns ≥ 0.05.