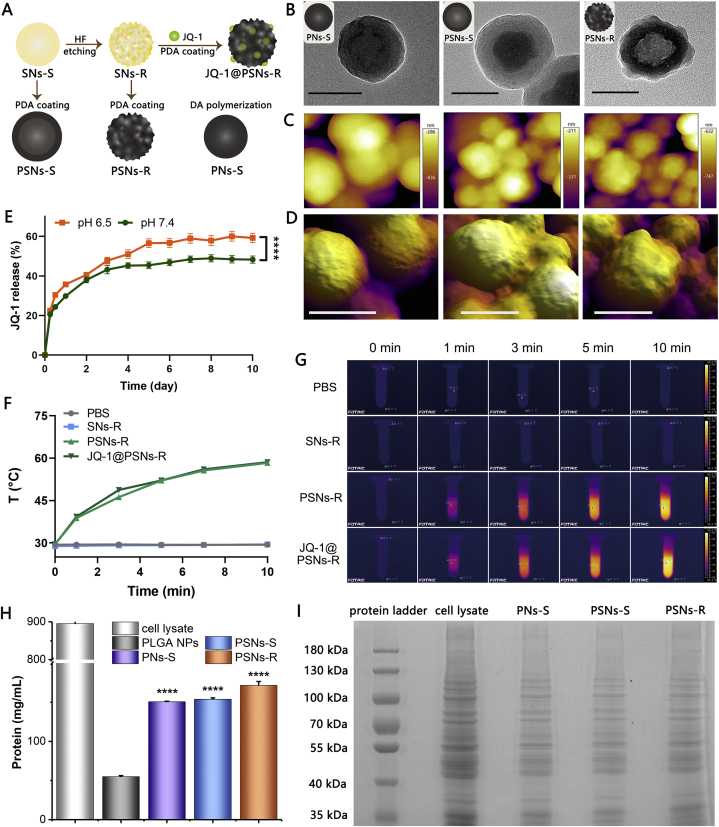
Figure 1.
Characterization of nanoparticles. (A) Schematic illustration of basic preparation steps and nanoparticles. (B) Transmission electron microscopy images of PNs-S, PSNs-S and PSNs-R. Scale bar = 100 nm. (C) Atomic force microscopy images of PNs-S, PSNs-S and PSNs-R. (D) The 3D images of PNs-S, PSNs-S and PSNs-R. Scale bar = 100 nm. (E) Released JQ-1 from JQ-1@PSNs-R under different pH conditions (data were mean ± SEM, n = 3 and analyzed by two-way ANOVA. ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001). (F) Temperature rise curves of PBS, SNs-R, PSNs-R and JQ-1@PSNs-R after 808 nm laser irradiation. (G) Photo-thermal conversion capacity of PBS, SNs-R, PSNs-R and JQ-1@PSNs-R. (H) The ability of PLGA NPs, PNs-S, PSNs-S and PSNs-R to adhere to cell lysate (data were mean ± SEM, n = 4 and analyzed by one-way ANOVA. ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001). (I) The SDS-PAGE result to show the adsorbed protein components of PNs-S, PSNs-S and PSNs-R.