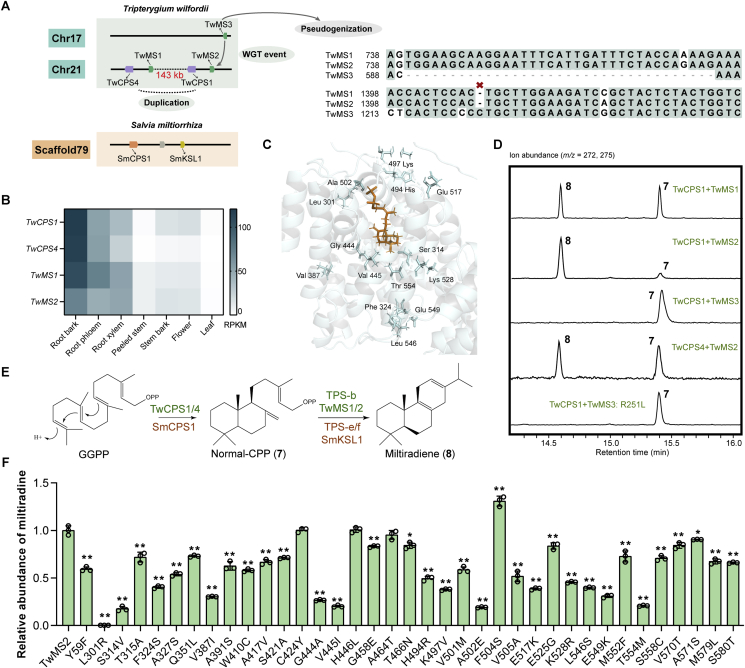
Figure 5.
Mechanisms driving the functional evolution of TwMSs. (A) The process of gene duplication of TwMSs. (B) Gene expression of TwCPS1/4 and TwMS1/2 in different tissues. (C) Protein model of TwMS2. Blue cartoons represent the protein model of TwMS2, orange sticks represent the substrate normal-CPP. Blue sticks represent residues that differ in the amino acid sites of TwMS1/2 and TwMS3, and the production of miltiradiene after mutation is 50% lower than that of the wild type. (D) GC–MS analysis of the products of TwMSs and TwCPS1/4. (E) Reactions catalyzed by TwCPS1/4 and TwMS1/2. (F) Relative abundance of miltiradiene in strains expressing TwMS2 and its mutants. Data are mean ± SD, n = 3; ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01 by Student's t-test.