Figure 3.
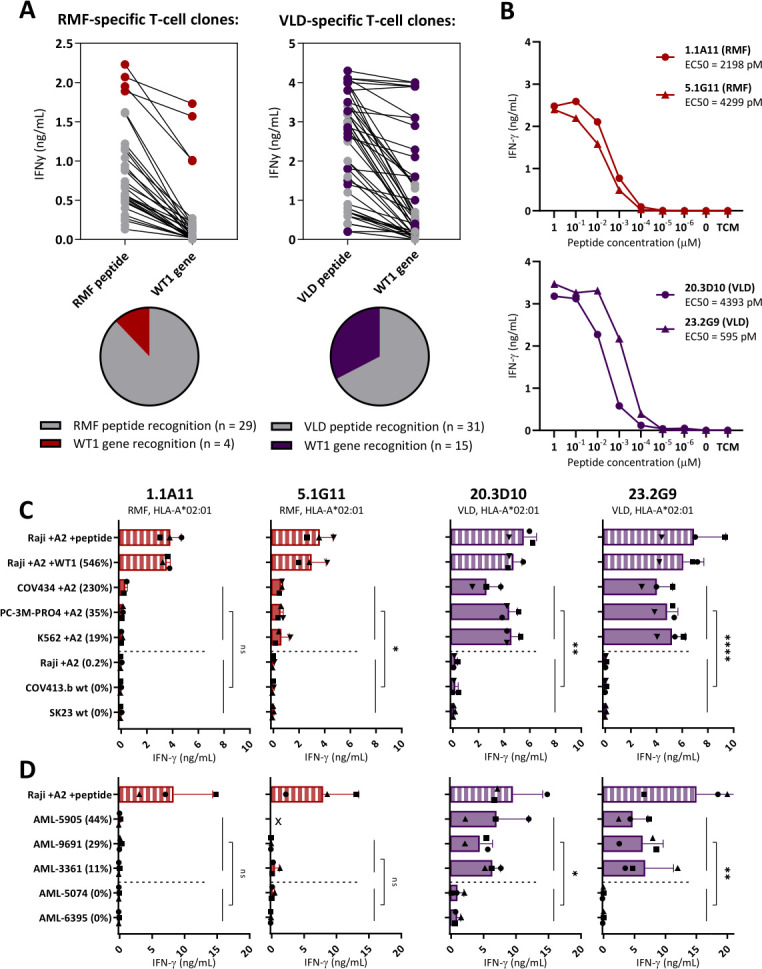
Limited WT1-specific reactivity of the RMF-specific T-cell clones. Comparison of T-cell clones recognizing the RMFPNAPYL (RMF) and VLDFAPPGA (VLD) peptide, both presented in HLA-A*02:01. (A) IFN-γ production (ng/mL) of T-cell clones recognizing Raji pulsed with RMF/A2 or VLD/A2 peptide (1 µM) identified in five healthy donors. T-cell clones also recognizing Raji transduced with WT1 (WT1 gene) on a similar level (>50%), are depicted with colored dots. (B) The four most potent T-cell clones stimulated overnight with Raji pulsed with titrated peptide. EC50 values represent the peptide concentrations needed to induce 50% of the maximum cytokine production, and values were calculated based on sigmoidal curves. (C) T-cell clones stimulated overnight with tumor cell lines (E:T=1:6). All cell lines express the HLA-A*02:01, either wildtype (wt) or introduced by transduction (+A2). Percentage relative WT1 expression is depicted, as determined by RT-qPCR. (D) T-cell clones stimulated overnight with primary AML patient samples (E:T=1:16). (x=Recognition of AML-5905 is not shown for clone 5.1G11, since this sample is HLA-B*35:01 positive and the 5.1G11 clone demonstrated allo-HLA reactivity against this allele in an EBV-LCL panel). (C, D) Symbols represent averaged duplicate values from three independent experiments. Mean and SD are depicted. WT1+ and WT1- targets were grouped, and reactivity of WT1 T-cell clones directed against these groups were compared using an unpaired t-test (two-sided). AML, acute myeloid leukemia; EBV-LCL, Epstein-Barr virus transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines; ns, not significant.
