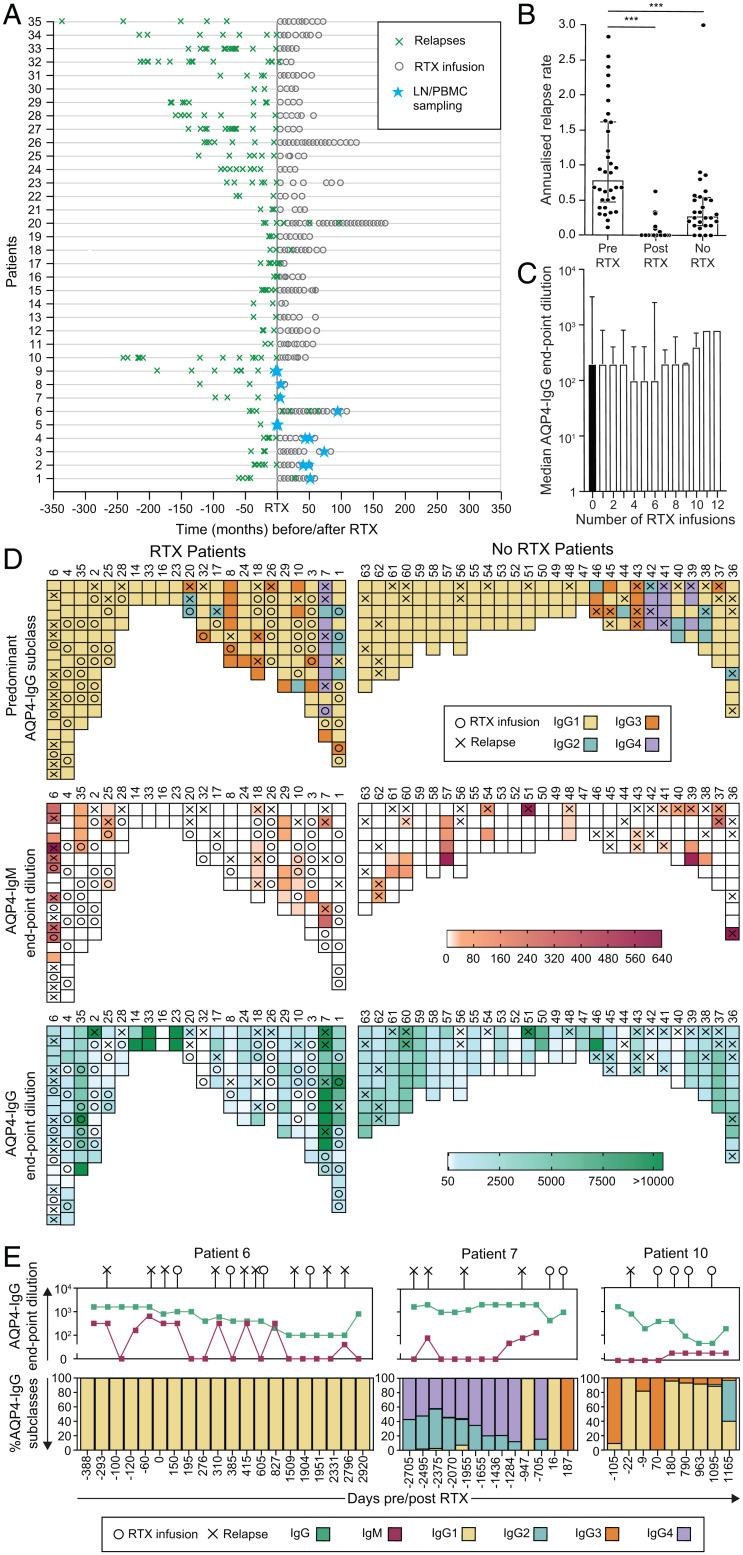
Fig. 1.
Serological associations with relapses and RTX administration in patients with NMOSD. (A) The effect of RTX administration on relapses (green crosses) in 35 NMOSD patients administered RTX at time 0. The timing of paired LN and PBMC sampling is shown (blue stars). (B) Mean ARR at last follow-up compared between patients before RTX and after RTX (P < 0.001) and to those administered no RTX (P < 0.001, Mann–Whitney U tests). (C) AQP4-IgG serum endpoint dilutions (shown as reciprocal of 1:dilution) were not reduced after multiple infusions of RTX (P = 0.99, Kruskal–Wallis test). (D) Heat maps to represent associations between relapses (X) and the dominant AQP4-IgG subclass (>50% of total AQP4-IgG, Top; determined by flow cytometry), AQP4-IgM (Middle; levels in red; determined by end-point titrations using live cell–based assays), and total AQP4-IgG (Bottom; levels in green; by endpoint titrations using live cell–based assays) in patients either administered RTX (n = 22) or naive to RTX (n = 28). (E) Longitudinal data in individual NMOSD patients (6, 7, 10), with negative values indicating days before the first RTX infusion; ***P < 0.001.