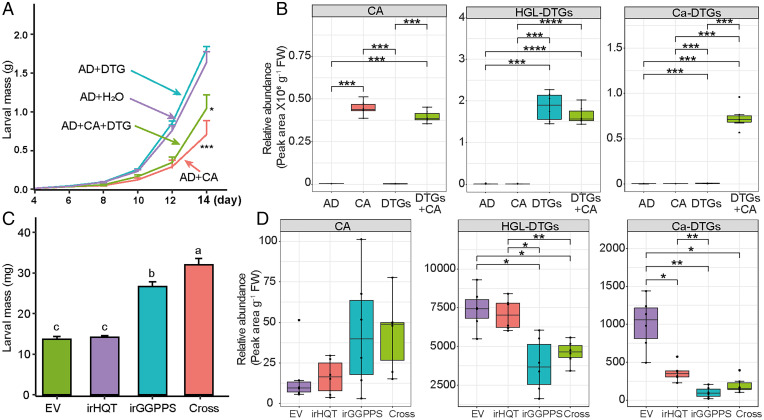
Fig. 3.
M. sexta larvae use CA and HGL-DTGs to detoxify each other. (A) Mass (mean + standard error (SE), n = 13–15) of M. sexta larvae fed AD supplemented with 1.2 mg g−1 CA, 2 mg g−1 HGL-DTGs (also abbreviated DTG or DTGs in the figure image), or both CA and HGL-DTGs, compared with AD supplied with only water (H2O) as control (Con). (B) Relative abundances (n = 5) of CA, HGL-DTGs, and caffeoylated DTGs (Ca-DTGs) in the frass of M. sexta larvae that fed on different AD. (C) Mass (mean + SE, n = 36–40) of M. sexta larvae fed hemizygous transgenic irHQT, irGGPPS plants, or an irHQT x irGGPPS Cross for 4 d. (D) The relative abundances (n = 5) of CA, HGL-DTGs, and Ca-DTGs in the frass of M. sexta larvae that fed on different transgenic plants. Asterisks indicate significant differences among different groups (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; Student t test with Bonferroni correction). (B and D) The upper whisker extends from the hinge to the largest value no further than 1.5 * interquartile range (IQR) from the hinge and the lower whisker extends from the hinge to the smallest value at most 1.5 * IQR of the hinge.