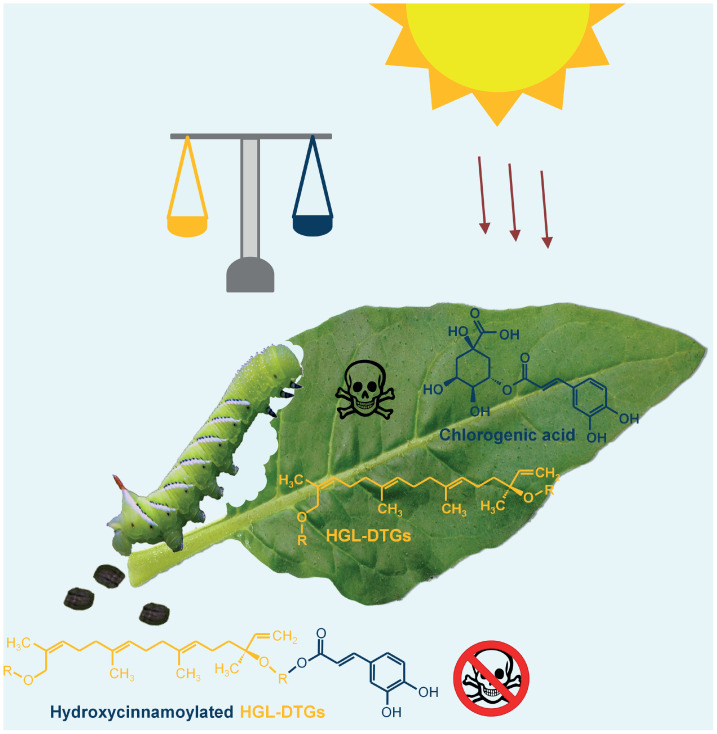
Fig. 5.
Postingestive interactions between diterpenoids and phenolics allow caterpillars to detoxify both defense pathways, while plants balance opposing selection pressures to minimize this detoxification process. Plants produce diverse specialized metabolites to deal with biotic and abiotic stresses from environments, such as diterpenoids (yellow) and phenolic CA (blue), both of which have deterrent effects on caterpillar feeding. Phenolics also function as sunscreens that protect plants from UV-B radiation. When fed these two toxic compounds, larvae of specialized insects can reesterify the phenolic moiety of CA onto the diterpenoid defenses and prevent the antiherbivore function of both defense compound classes. In nature, plants can balance the abundances of diterpenoids and phenolics to circumvent the detoxification of specialized insects and optimize UV protection.