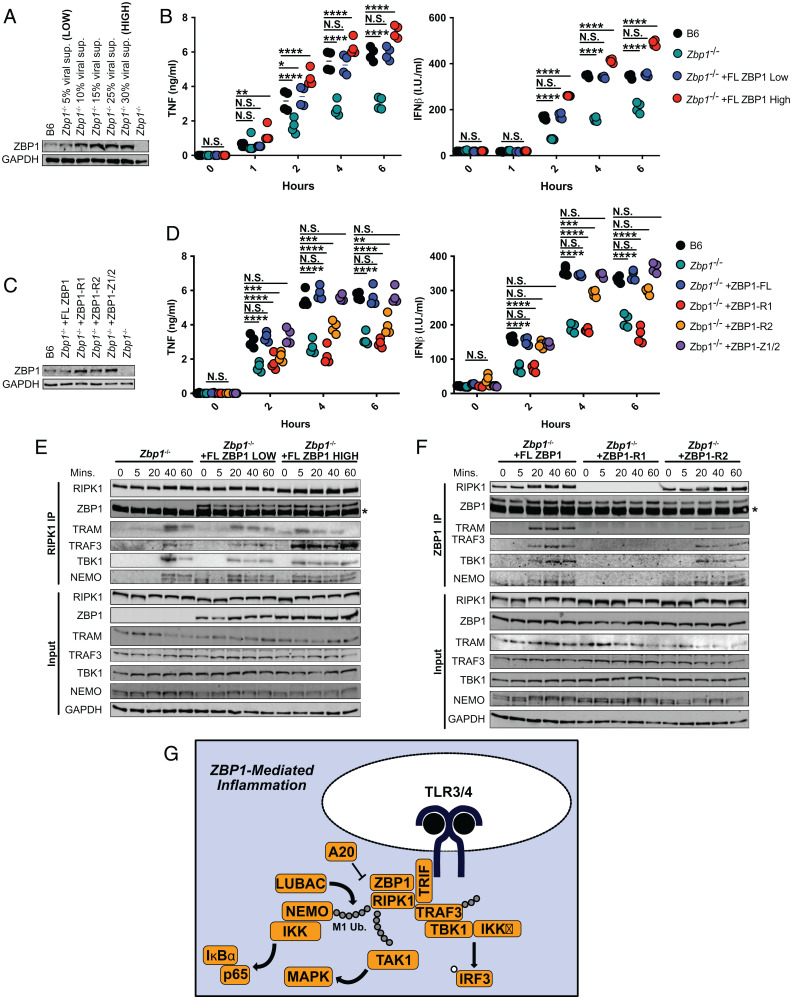
Fig. 5.
ZBP1 levels modulate RHIM-mediated inflammatory responses. (A) ZBP1 levels in B6 and Zbp1−/− macrophages transduced with indicated concentrations of viral supernatant for ZBP1. (B) TNF and IFNβ protein levels in B6, Zbp1−/−, and Zbp1−/− macrophages reconstituted with low or high levels of ZBP1. (C) ZBP1 levels in Zbp1−/− macrophages transduced with mutant ZBP1 constructs lacking RHIM1 (ZBP1-R1), RHIM2 (ZBP1-R2), or both Zɑ domains. (D) TNF and IFNβ protein levels in B6, Zbp1−/−, and Zbp1−/− macrophages reconstituted with RHIM or Zɑ mutant ZBP1 constructs. (E) RIPK1 immunoprecipitation in Zbp1−/− macrophages reconstituted with low and high levels of ZBP1 and probed for proinflammatory complex components. Asterisk indicates band from antibody heavy chain. (F) ZBP1 immunoprecipitation in Zbp1−/− macrophages reconstituted with full-length or RHIM-mutant ZBP1 and probed for proinflammatory complex components. Asterisk indicates band from antibody heavy chain. (G) Model of ZBP1-regulated complex formation leading to inflammation and cell death in response to LPS. Data from immunoblots are representative of three or more biologically independent experiments. Unless otherwise indicated, blots were singly or doubly probed to ensure highest quality. All blots from a specific panel are run from a single set of lysates that were identically handled. For ELISA data, data points indicate the mean from triplicate wells of four biologically independent experiments. ANOVA was used for comparison between groups: ns, nonsignificant (P > 0.05); *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.