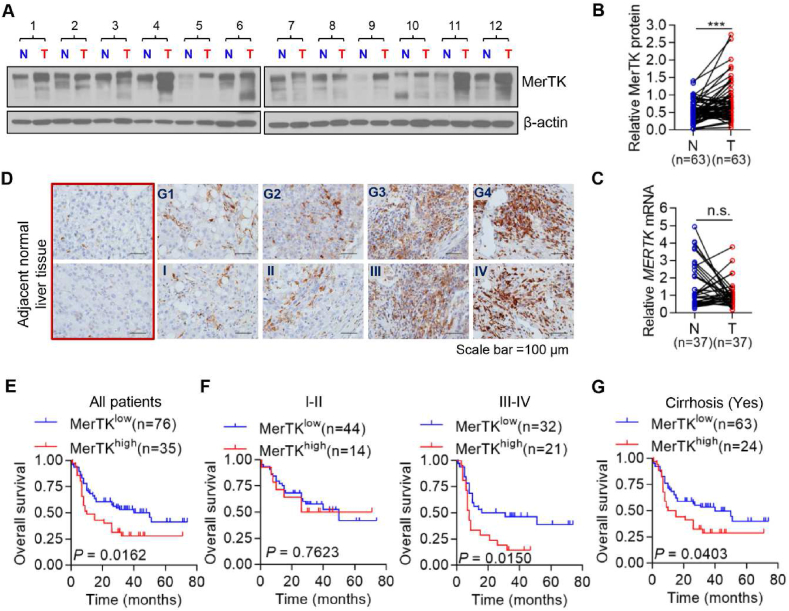
Fig. 1.
Aberrant MerTK expression in HCC and high expression of MerTK were associated with poor outcomes in HCC Patients. (A) Relative MerTK protein expression in HCC tumor adjacent normal (N) and matched tumor tissues (T) was examined by Western blot (n = 63). (B) Relative MerTK protein expression of Western blot analyses was quantified using Image J and normalized to the β-Actin (n = 63). Data are presented as mean ± SD, statistical significance was determined by paired Student's t-test. ***P < 0.001. (C) MERTK mRNA expression in HCC tumor adjacent normal (N) and matched tumor tissues was detected by using qRT-PCR (n = 37). Data are presented as mean ± SD, statistical significance was determined by paired Student's t-test. n. s., not significant. (D) IHC staining of MerTK protein in HCC tumor tissues. Representative MerTK IHC staining photomicrographs (400 × ) of normal liver tissue, Grade 1 (G1), Grade 2 (G2), Grade 3 (G3) and Grade 4 (G4) HCC tumor tissues (upper panel), and TNM stage I, II, III and IV HCC tumor tissues (lower panel), are shown. (E) Kaplan-Meier analysis of the OS of HCC patients with high (n = 35) or low MerTK (n = 76) expression. (F) Kaplan-Meier overall survival analysis of HCC patients diagnosed with I-II (n = 58) or III-IV (n = 53) stage according to MerTK protein expression. (G) Kaplan-Meier OS curve analysis of HCC patients diagnosed with Cirrhosis (n = 87) according to MerTK protein expression.