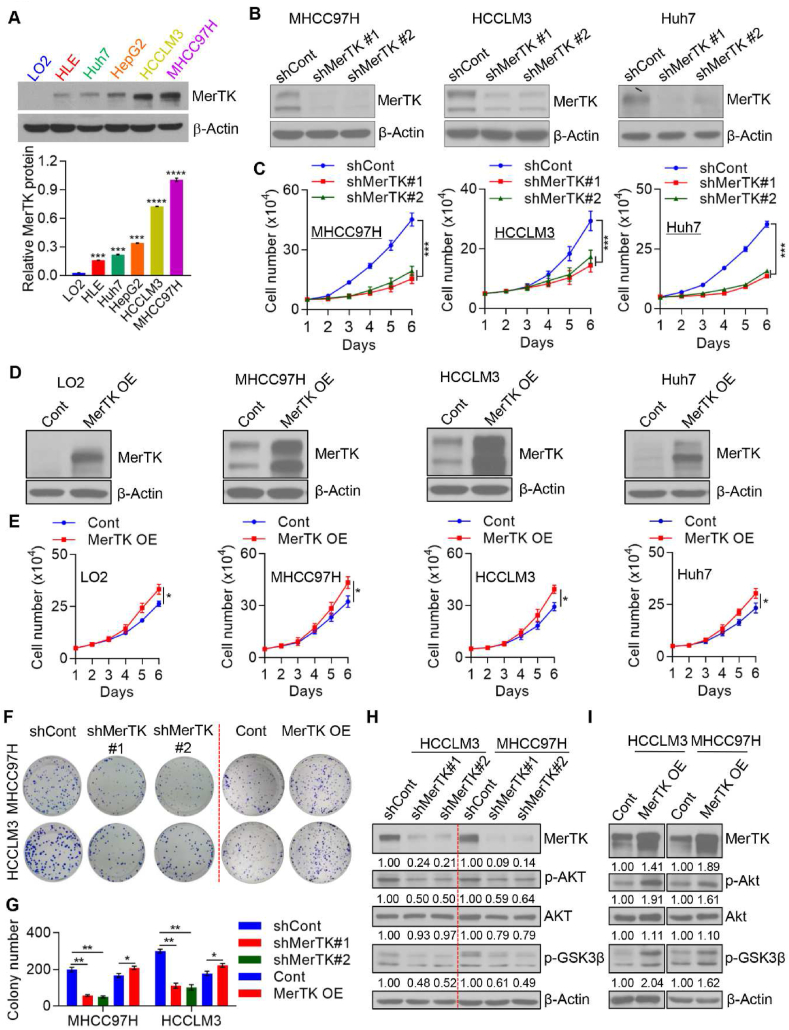
Fig. 2.
MerTK is crucial for HCC cell proliferation. (A) Western blot analysis and quantification of MerTK expression in total cell extracts in LO2, HLE, Huh7, HepG2, HCCLM3, and MHCC97H cells. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments, statistical significance was assessed by One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, ***P < 0.001. (B) Western blot analysis demonstrating MerTK stable knockdown in the indicated HCC cells transfected with shRNA specific to MERTK mRNA. (C) Cell proliferation of MerTK stable knockdown MHCC97H, HCCLM3, and Huh7 cells lines was measured by cell counting. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments, statistical significance was assessed by One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, ***P < 0.001. (D and E) Western blot analysis demonstrating MerTK overexpression in LO2 cells and the indicated HCC cells (D). Cell proliferation of MerTK overexpression LO2, MHCC97H, HCCLM3, and Huh7 cells lines were measured by cell counting (E). Cont, refers to cells transduced with empty vector and hereafter; MerTK OE, refers to cells transduced with plasmid overexpressing MerTK and hereafter. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments, statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test, *P < 0.05. (F and G) Representative images (F) and quantification (G) of colony formation assay of MerTK stable knockdown or overexpression MHCC97H and HCCLM3 cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD, statistical significance was assessed by One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test and Student's t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (H and I) Immunoblots of tumor growth related proteins p-GSK3β, p-Akt, Akt in MerTK stable knockdown (H) or overexpression (I) MHCC97H and HCCLM3 cells. β-Actin was used as a loading control.