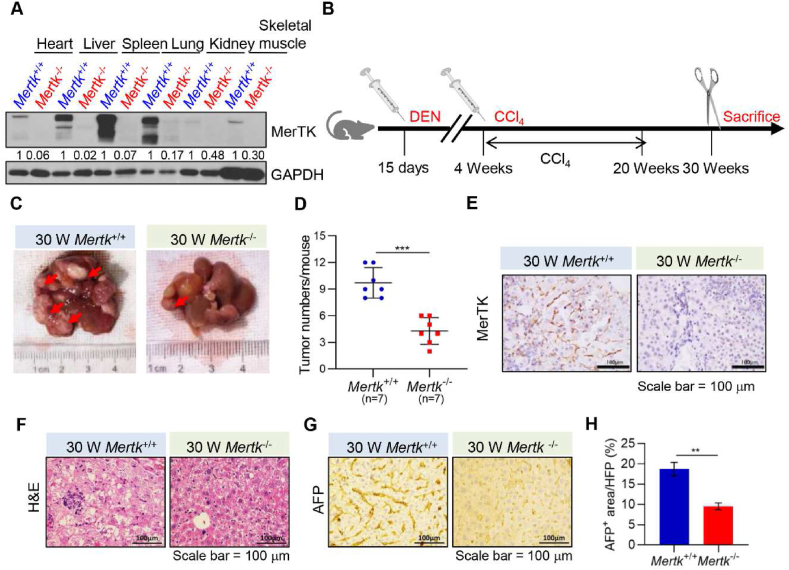
Fig. 5.
Deletion of MerTK Inhibits DEN and CCl4-Induced HCC Formation
(A) Lysates of all tissues from Mertk+/+ and Mertk−/− mice were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against MerTK or GAPDH at 30 weeks of age. GAPDH served as a loading control. (B) Schematic representation of DEN and CCl4-treated Mertk+/+ and Mertk−/− mice. At 15 days of age, mice were injected with DEN. At 4 weeks of age, mice were injected with CCl4 once a week for 16 weeks, mice were sacrificed at 30 weeks. (C) Representative macroscopic pictures of livers from Mertk+/+ and Mertk−/− mice at 30 weeks of age. Arrowhead indicates tumor nodules. (D) Quantification of liver tumors in Mertk+/+ and Mertk−/− mice at 30 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SD, statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test, ***P < 0.001. (E) Immunohistochemical analysis of liver sections for MerTK expression from Mertk+/+ and Mertk−/− mice at 30 weeks of age. Images were obtained at 40 × magnification. (F) Histological analysis (H&E) of livers from Mertk+/+ and Mertk−/− mice at 30 weeks of age. Images were obtained at 40 × magnification. (G) Immunohistochemical analysis of liver sections for AFP expression from Mertk+/+ and Mertk−/− mice at 30 weeks of age. Images were obtained at 40 × magnification. (H) Quantification of positive areas per field in (F) was determined by Image J software. Data are presented as mean ± SD, statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test, **P < 0.01.