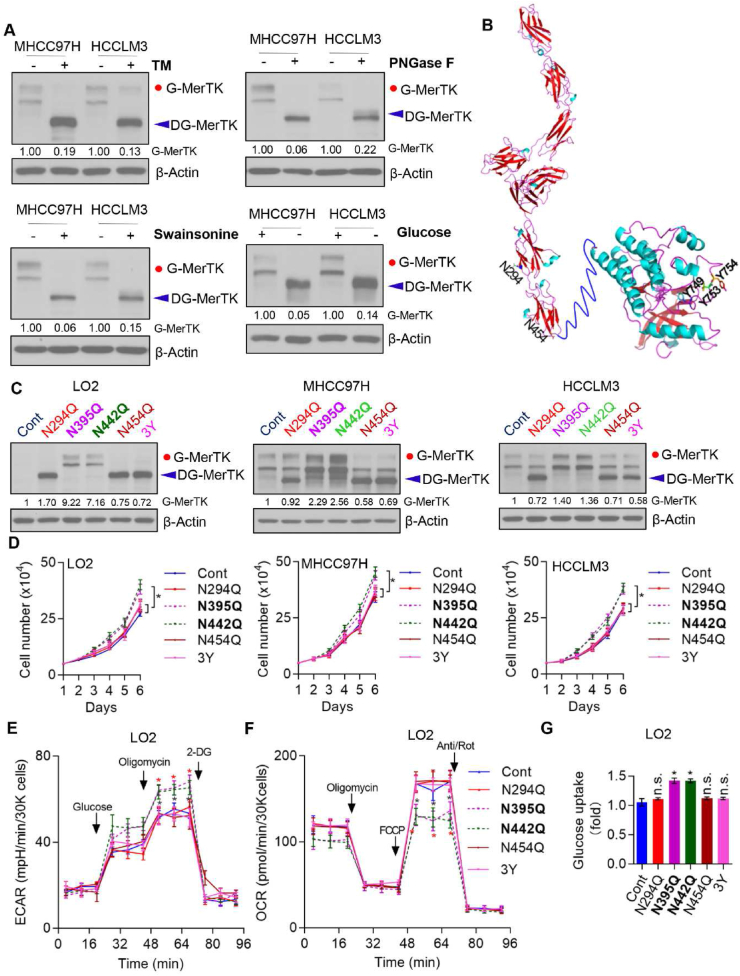
Fig. 6.
N-Glycosylation of MerTK is Essential for HCC Cell Growth. (A) Western blot analysis of MHCC97H, HCCLM3 treated with or without Tunicamycin (TM), PNGase F, Swainsonine and glucose starvation. (B) Structure of MerTK and the modification site of N294Q, N454Q and 3Y. (C and D) MerTK expression was detected by Western blot in LO2, MHCC97H and HCCLM3 cells transfected with the N294Q, N395Q, N442Q, N454Q and 3Y mutant plasmids, respectively (C). Cell proliferation was analyzed by cell counting (D). Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments, statistical significance was assessed by One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, *P < 0.05. (E and F) The intact cellular ECAR and OCR of WT and indicated MerTK mutant LO2 Cells were measured in real time using the Seahorse XF96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer. Data are presented as mean ± SD, statistical significance was assessed by One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, *P < 0.05. (G) Glucose uptake of WT and MerTK indicated mutant LO2 Cells by 2-NBDG incorporation by flow cytometry. Data are presented as mean ± SD, statistical significance was assessed by One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, *P < 0.05, n. s., not significant.