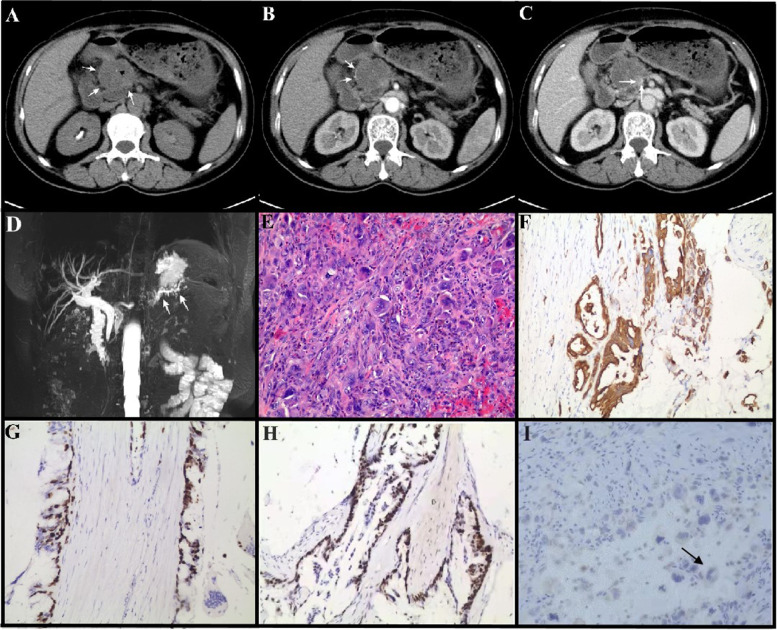
Fig. 1.
Imaging and pathological analysis of pca_ai1 patient. A-C, CT images. Dedicated abdominal CT found an enlarging exophytic 4.5-cm pancreatic head mass (white arrow) with focal calcification (black arrowhead, A). The lesion showed heterogenous low intensity in the edge (arrow, B) relative to pancreatic parenchyma in the pancreatic and portal vein phases with directly protruding into the adjacent superior mesenteric vein (arrow, C). D, MRI analysis. A filling defect in the main pancreatic duct (MPD) of the pancreatic head and dilation of the MPD distal to the lesion are evident in MRI, and indicated by arrows in D. E, Representative images of H&E staining of surgical removed pancreatic tissue of pca_ai1. Arrows indicated osteoclast-like giant cells (OGCs). F-I, Representative images of IHC staining of surgical removed pancreatic tissue of pca_ai1. pan-cytokeratin (CKpan) (F), Ki67 (G), p53 (H), and CD68 (I) were used to indicate pleomorphic neoplastic cells and OGCs. Arrows in H indicated osteoclast-like giant cells (OGCs) with CD68 positive staining. Bar = 200 µm