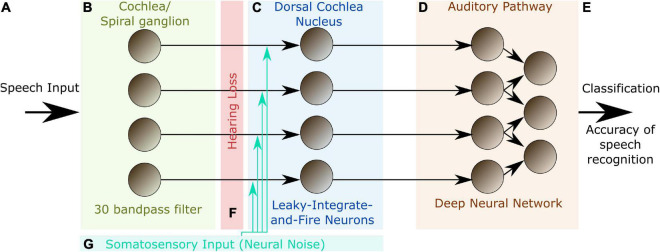
FIGURE 1.
Model layout. The complete model consists of three different modules representing different stages of the auditory pathway in the human brain. The input to the model are single words encoded as wave files with a sampling rate of 44.1 kHz and 1 s duration (A). The cochlea and the spiral ganglion are modeled as an array of 30 band-pass filters (B). The continuous output signal of (B) serves as input to 30 leaky integrate-and-fire-neurons representing the DCN (C). The spike-train output of the DCN model is down sampled and serves as input for a deep neural network that is trained with error backpropagation on the classification of 207 different German words (D). The classification accuracy serves as a proxy for speech recognition (E). In order to investigate the effect of a particular hearing loss, the cochlea output amplitude is decreased by a certain factor independently for all frequency channels (F). White noise representing somatosensory input to the DCN can be added independently to the input of the different leaky-integrate-and-fire-neurons (LIF, G).