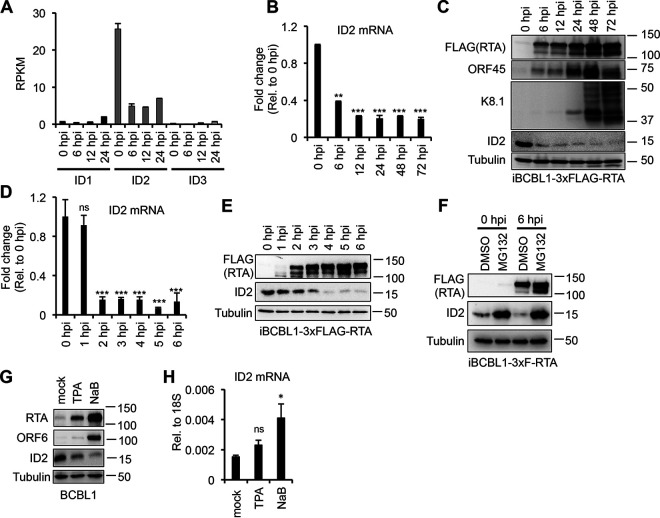
FIG 1.
ID2 is rapidly downregulated during KSHV lytic reactivation. (A) Transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis of the expression of ID genes during KSHV lytic reactivation at various time points in iBCBL1-3xFLAG-RTA cells. The average of three biological replicates is shown. (B) ID2 gene expression was measured by RT-qPCR in iBCBL1-3xFLAG-RTA during latency and at various time points of lytic reactivation. (C) Immunoblot analysis of ID2 and lytic viral protein expression during KSHV lytic reactivation in iBCBL1-3xFLAG-RTA cells. (D) RT-qPCR analysis of ID2 gene expression during KSHV latency (0 hpi) up to 6 hpi in iBCBL1-3xFLAG-RTA cells. (E) Western blot analysis of FLAG-RTA and ID2 expression in reactivated iBCBL1-3xFLAG-RTA cells. (F) Immunoblot analysis of 3xFLAG-RTA and ID2 protein expression during MG132 or DMSO (vehicle control) treatment of reactivated iBCBL1-3xF-RTA cells at 0 (latency) and 6 hpi. (G) Immunoblot analysis of lytic viral proteins and ID2 expression at 24 hpi in BCBL1 in which lytic reactivation was induced with TPA or NaB. (H) RT-qPCR testing of ID2 gene expression during TPA- and NaB-mediated KSHV reactivation in BCBL1 cells at 24 hpi. t tests were performed between GFP-OE and ID2-OE (sample of n = 3), and degree of statistical significance is indicated as *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; and ns, not significant.