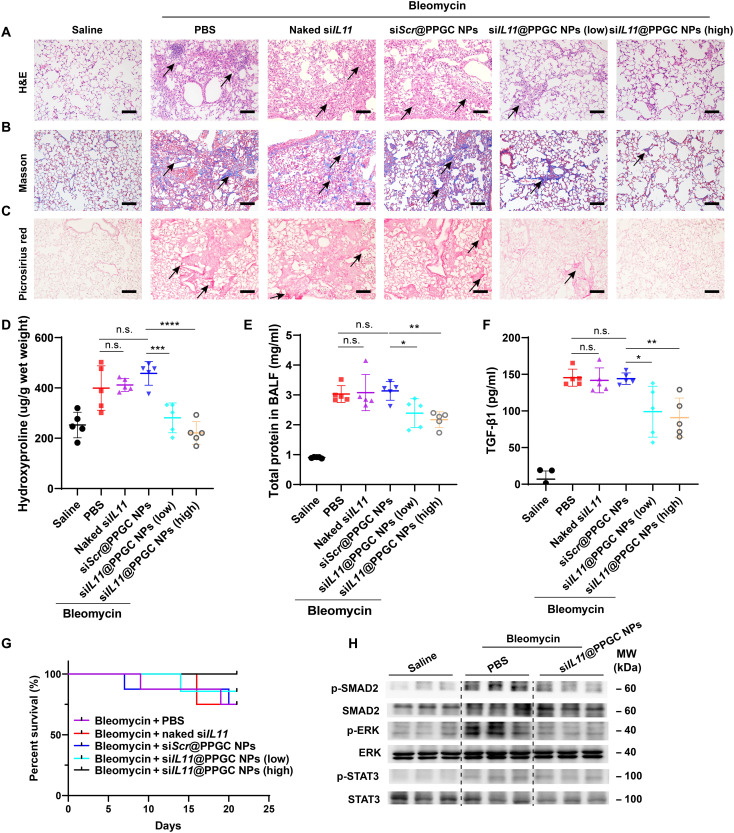
Fig. 7. In vivo therapeutic validation of inhaled siRNA therapeutic–mediated IL-11 down-regulation in a pulmonary fibrosis model.
(A to C) Histological analysis of lung sections, including H&E staining (A), Masson’s trichrome staining [muscle fibers and erythrocytes (red), collagen (blue), and nuclei (black-purple)] (B), and Picrosirius red staining (collagen types I and III) (red) (C). Scale bars, 50 μm. (D) Measurement of hydroxyproline content in mouse lung tissues (N = 5). (E) Determination of total protein content in BALF using BCA assay (N = 5). (F) ELISA quantification of TGF-β1 level in BALF (N = 5). (G) Survival curve of bleomycin-induced fibrosis animals after treatment with PBS, siScr@PPGC NPs, naked siIL11, or siIL11@PPGC NPs (N = 8). (H) Western blotting assay of phosphorylation and total expression of SMAD2, ERK, and STAT3 in lung tissue homogenates collected from different groups. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping standard. Significant differences were assessed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey test (D to F). Survival analysis was performed using a log-rank test (G). Results are presented as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, n.s., not significant, P > 0.05.