FIGURE 1.
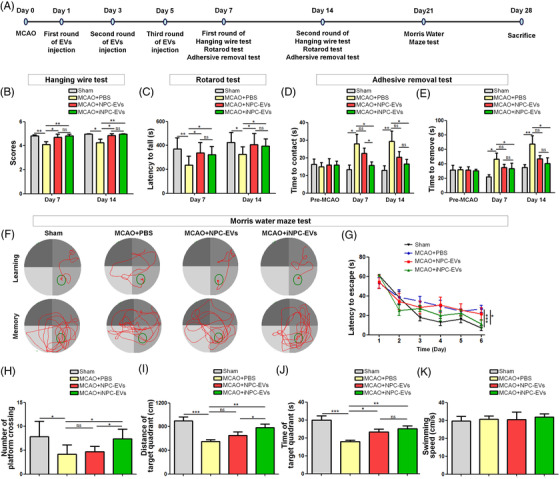
Post‐stroke administration of induced neural stem/progenitor cell (iNPC)‐extracellular vesicles (EVs) improves neurological functions after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Mice received intravenous injection of 300 μl EVs (0.5 μg/μl) or PBS 24 h after 30‐min MCAO and at 2 days intervals on days 1–5 after stroke. (A) Experimental design. (A–E) Sensorimotor functions were assessed up to 14 d after MCAO or sham operation via hanging wire test (B), rotarod test (C), and adhesive removal test (D and E). (F–K) Long‐term cognitive functions were evaluated in the Morris water maze. (F) Representative images of the swim paths of mice in each group. The escape times (G, learning), the time spent (H)/distance traveled (I)/platform crossing numbers (J) in the target quadrant (memory), and the swim speed (K) were recorded. n = 9–13/group. Error bars denote s.d.. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001, and ****p < .0001. ns denotes non‐significance. The statistical difference among groups was assessed with the parametric one‐way the analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Bonferroni test.
