FIGURE 2.
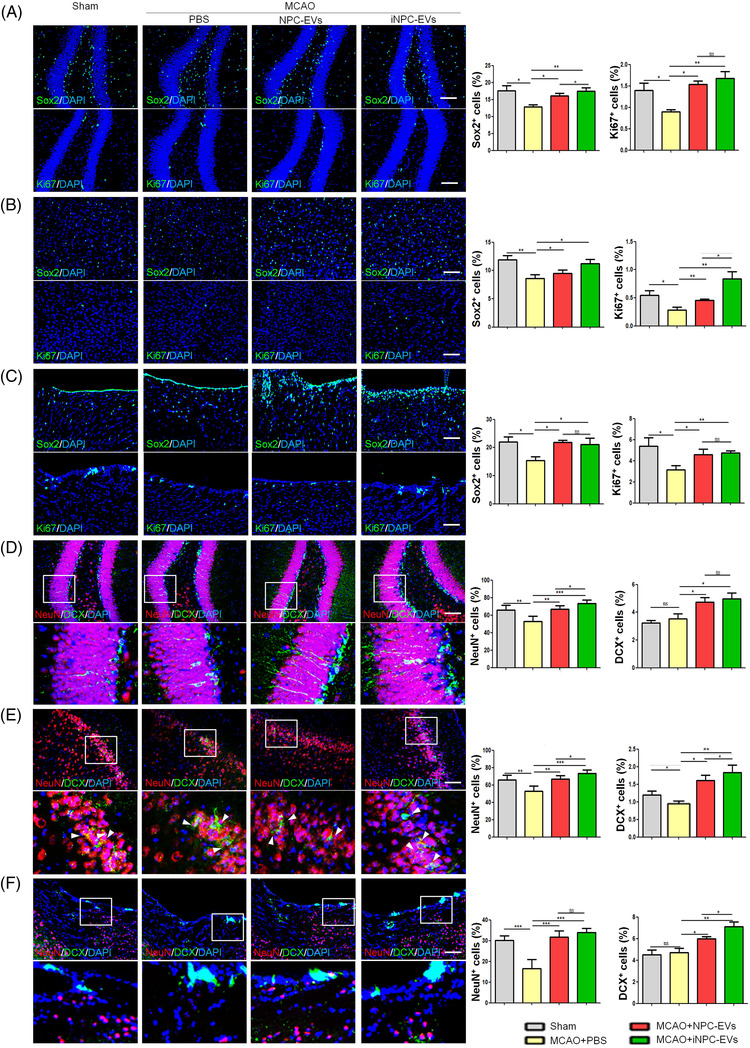
Post‐stroke administration of induced neural stem/progenitor cell (iNPC)‐extracellular vesicles (EVs) improves neurogenesis, inhibits neuroinflammation and represses apoptosis. Focal cerebral ischemic brains treated with or without EVs, and their sham controls were collected on day 28 after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). (A–C) Representative confocal microscopy images of Sox2 (green) and Ki67 (green) in the hippocampus (A), peri‐infarct cortex (B) and sub‐ventricular zone (SVZ) (C). Proportions of cells with Sox2 and Ki67 immunoreactivities in each group were given on the right panel (n = 4). (D–F) Representative confocal microscopy images of DCX (green) and NeuN (red) in the hippocampus (D), peri‐infarct cortex (E), and SVZ (F). Proportions of cells with DCX and NeuN immunoreactivities in each group were given on the right panel (n = 4). Scale bar: 100 μm. Error bars denote s.d.. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001 and ****p < .0001. ns denotes non‐significance. The statistical difference among groups was assessed with the parametric one‐way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test
