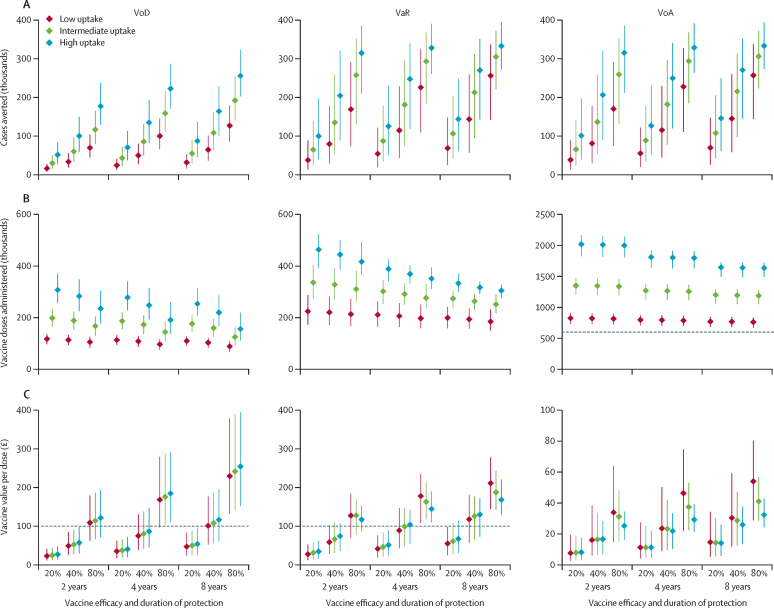
Figure 3.
Effects of vaccine uptake, efficacy, and duration of protection on the impact and cost-effectiveness of three vaccination strategies against gonorrhoea in men who have sex with men in England over 10 years
(A) Total cases averted by vaccination. (B) Total number of vaccine doses administered. (C) Value of vaccination per dose administered. Columns of panels correspond to the three targeting strategies assessed (VoD, VaR, and VoA). Three levels of efficacy (20%, 40%, or 80%) and three durations of protection (2, 4, or 8 years) are represented along the x-axis. Different coloured bars correspond to three different levels of uptake: the low-uptake scenario (16·5% [95% CI 16·3–16·7]), which is half the level of HPV vaccine uptake by MSM in sexual health clinics in England (ie, 33·0% [32·7–33·3], labelled intermediate on the graph), and one-quarter the level of the high-uptake scenario (66·0% [65·4–66·6]). Points show medians and bars show 95% credible intervals. Note that panels A and B show undiscounted numbers while panel C shows discounted £ values. Also note that in panel B, the dashed line in the VoA graph shows the upper limit of the y-axis scales of the VoD and VaR graphs, and in panel C, the dashed lines in the VoD and VaR graphs show the upper limit of the y-axis scale of the VoA graph. VoD=vaccination on diagnosis. VaR=vaccination according to risk. VoA=vaccination on attendance.