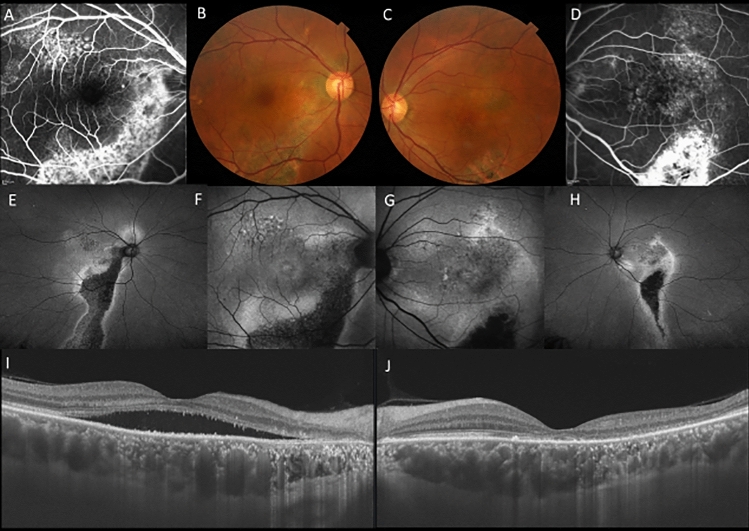
Figure 3.
A 56-year-old male patients with central serous chorioretinopathy in both eyes. (A) In the right eye, staining was seen along the inferior arcade vessel by fluorescein angiography (FA). (B) In the right eye, color fundus photography showed retinal pigment epithelial atrophy in the area corresponding to staining on FA. (C) In the left eye, color fundus photography color fundus photography showed retinal pigment epithelial atrophy inferior to the macula. (D) In the left eye, staining was seen at the inferior arcade vessel by FA. (E) Widefield fundus autofluorescence clearly showed descending tract extending inferiorly in the right eye. (F) Fundus autofluorescence suggested the presence of exudation in hyperfluorescence area in the right eye. (G) Fundus autofluorescence suggested the presence of exudation or previous exudation in hyperfluorescence in the left eye. (H) Widefield fundus autofluorescence clearly showed descending tract extending inferiorly in the left eye. (I) Swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) showed presence of subretinal fluid and a dilated choroid in the right eye. (J) SS-OCT also showed a dilated choroid with resolution of subretinal fluid in the left eye.