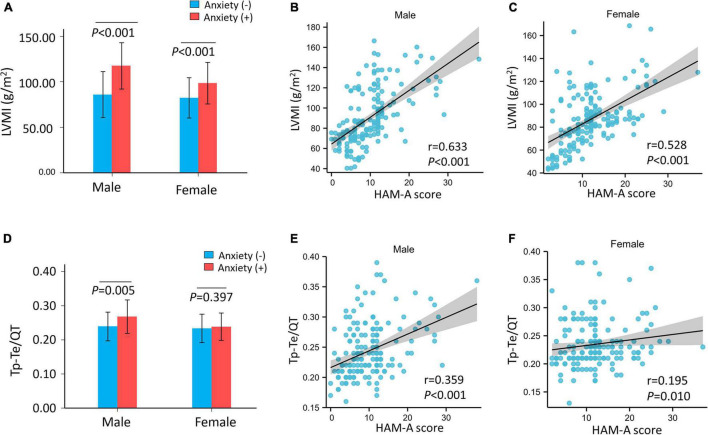
FIGURE 2.
The LVMI and Tp–Te/QT ratio of hypertensive patients and correlation with HAM-A score after stratified by sex. (A) The LVMI was significantly higher in hypertensive patients with anxiety than hypertensive patients without anxiety both in male (p < 0.001) and female (p < 0.001). (B,C) HAM-A score was significantly positive correlated with LVMI both in male (r = 0.633, p < 0.001) and female (r = 0.528, p < 0.001). The Tp–Te/QT ratio was significantly higher in hypertensive patients with anxiety than hypertensive patients without anxiety (p < 0.001). (D) Tp–Te/QT ratio was higher in male (p = 0.005) with anxiety but not in female (p = 0.397) with anxiety in hypertensive patients. (E,F) HAM-A score was positively correlated with Tp–Te/QT ratio (male: r = 0.359, p < 0.001; female: r = 0.195, p = 0.010). HAM-A, Hamilton anxiety scale; LVMI, left ventricular mass index; QT interval, Q wave start to T wave end interval; Tp–Te interval, T-wave peak to T-wave end interval.