Figure 1.
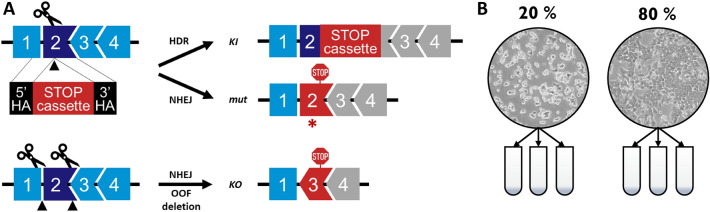
Sample preparation: (A) A schematic illustration of the strategies for CRISPR/Cas9 mediated generation of constitutive gene knockouts in HCT116 cells. Upper panel: Single guide RNA targeting an early exon of a gene of interest will generate a double-strand break (DSB). In the presence of a DNA repair donor containing a promoterless gene trap (stop) cassette flanked with 5’ and 3’ in-frame homology arms (HA) two DSB repair outcomes are possible: (1) homology-directed repair (HDR) will result in an in-frame knockin (KI) of the stop cassette leading to gene inactivation or (2) the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair will generate INDEL mutation (mut, represented by an asterisk), leading to a premature stop codon (red stop sign). Lower panel: targeting introns flanking an early critical exon with two guide RNAs will lead to an out-of-frame (OOF) deletion of the critical exon. Following the NHEJ-mediated repair, a premature stop codon (red stop sign) will be created in the downstream coding sequence, leading to gene knockout (KO). (B) KO cell lines were grown to densities of 20% and 80% confluency and samples were collected in triplicates.