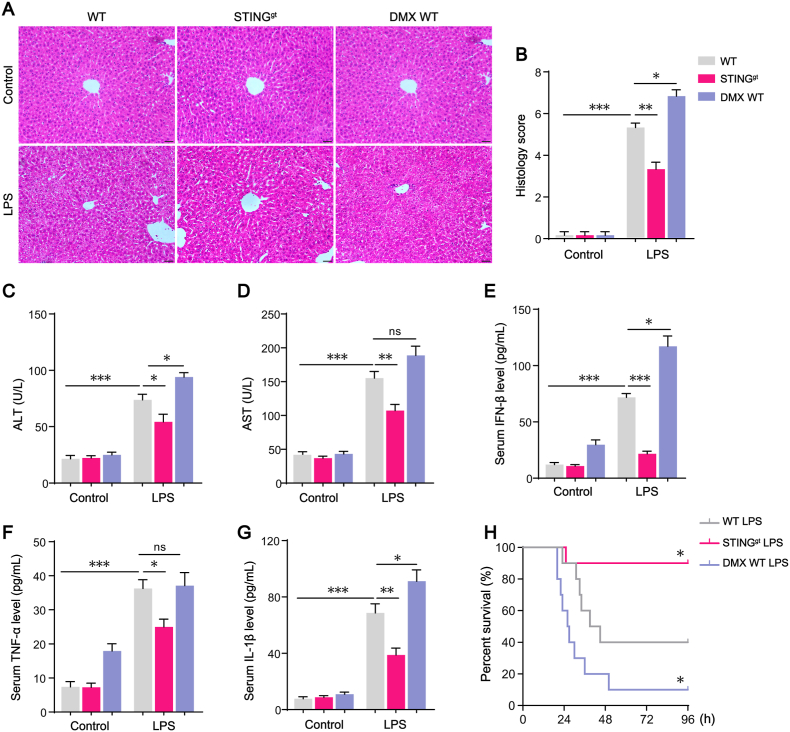
Fig. 2.
STING signaling activation plays a critical role in LPS-induced systemic inflammatory response and liver injury. (A–B) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and histology scores of liver sections in WT, STINGgt, or DMX-treated WT mice with or without LPS challenge (n = 6, bar = 20 μm). (C–D) ALT and AST concentrations in mouse serum in each group (n = 6). (E–G) Levels of inflammatory cytokines including IFN-β, TNF-α and IL-1β in mouse serum in each group (n = 6). (H) The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis after LPS (25 mg/kg) treatment in WT, STINGgt, or DMX-treated WT mice (n = 10). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns, no significance.