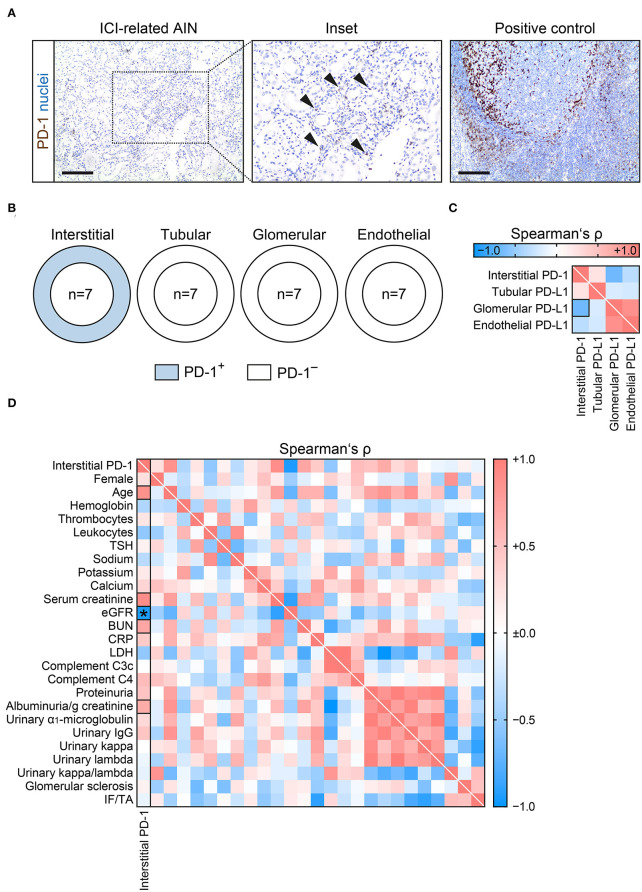
Figure 3.
PD-1 is present in interstitial cells and associates with kidney injury in ICI-related nephrotoxicity. (A) Interstitial cell PD-1 positivity (arrowheads) in AIN related to ICI therapy, tonsil tissue was used as positive control (scale bar: 200 μm). (B) Frequency of PD-1 positivity among different renal compartments. (C) Correlative analysis of interstitial PD-1 and PD-L1 positivity within different renal compartments in ICI-related nephrotoxicity are shown by heatmap reflecting mean values of Spearman's ρ. The rectangle box indicates a Spearman's ρ more than ±0.6. (D) Extent of interstitial cells positive for PD-1 in ICI-related nephrotoxicity in association with clinical and laboratory parameters are shown by heatmap reflecting mean values of Spearman's ρ. Rectangle boxes indicate a Spearman's ρ more than ±0.6, asterisks significant correlations in the stepwise linear regression analysis (p < 0.05). AIN, acute interstitial nephritis; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; C3c, complement factor 3 conversion product; C4, complement factor 4; CRP, C-reactive protein; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate (CKD-EPI); ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor; IF/TA, interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy; IgG, immunoglobulin G; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death protein 1-ligand 1; TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone.