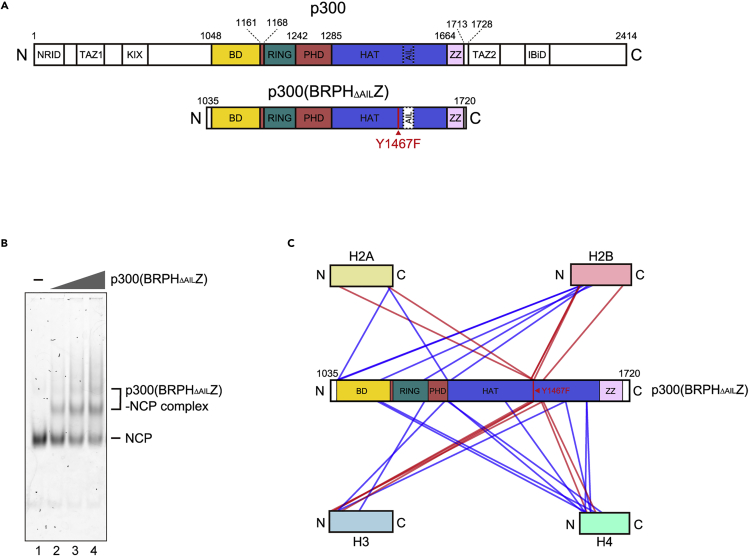
Figure 1.
p300(BRPHΔAILZ) binds to the NCP
(A) p300 and p300(BRPHΔAILZ) domain architectures. NRID: nuclear receptor interaction domain, TAZ1: transcriptional adaptor zinc-finger domain 1, KIX: kinase-inducible domain of CREB-interacting domain, BD: bromodomain, RING: really interesting new gene domain, PHD: plant homeodomain, HAT: histone acetyltransferase domain, AIL: autoinhibition loop, ZZ: ZZ-type zinc-finger domain, TAZ2: transcriptional adaptor zinc-finger domain 2, IBiD: IRF3-binding domain. p300(BRPHΔAILZ) has the Y1467F mutation and lacks the AIL.
(B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of p300(BRPHΔAILZ) and the NCP. The p300(BRPHΔAILZ)-NCP complex formation was analyzed by non-denaturing 4% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with SYBR Gold staining.
(C) Schematic representation of the results obtained by the crosslinking mass spectrometric analysis of the p300(BRPHΔAILZ)-NCP complexes. The inter-protein crosslinks between histones and p300(BRPHΔAILZ) are represented by lines. The crosslinks of the histone N-terminal regions with the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) residues near the HAT catalytic center are shown by red lines.