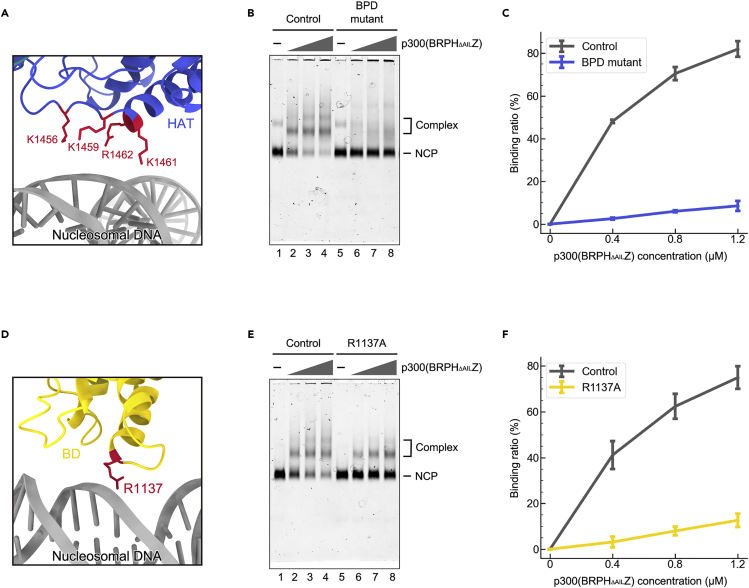
Figure 3.
NCP-binding activities of the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) mutants
(A) Close-up view of the interaction site between the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) HAT domain and the nucleosomal DNA.
(B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) BPD mutant (K1456A/K1459A/K1461A/R1462A) with the NCP. Complex formation was analyzed by non-denaturing 4% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with SYBR Gold staining. Lanes 1–4 are control experiments with p300(BRPHΔAILZ), and lanes 5–8 are experiments with the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) BPD mutant.
(C) Quantitative results of the NCP-binding activity of the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) BPD mutant. Ratios of the NCP bound to p300(BRPHΔAILZ) were estimated from the band intensity of the remaining free NCP, and the average values of three independent experiments (shown in panel (B) and Figure S5A) are plotted against the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) concentration. Data are displayed as mean value ±SD (n = 3 independent replicates).
(D) Close-up view of the interaction site between the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) bromodomain and the nucleosomal DNA.
(E) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) R1137A mutant with the NCP. Complex formation was analyzed by non-denaturing 4% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with SYBR Gold staining. Lanes 1–4 are control experiments with p300(BRPHΔAILZ), and lanes 5–8 are experiments with the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) R1137A mutant.
(F) Quantitative results of the NCP-binding activity of the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) R1137A mutant. Ratios of the NCP bound to p300(BRPHΔAILZ) were estimated from the band intensity of the remaining free NCP, and the average values of three independent experiments (shown in panel (E) and Figure S5B) are plotted against the p300(BRPHΔAILZ) concentration. Data are displayed as mean value ±SD (n = 3 independent replicates).