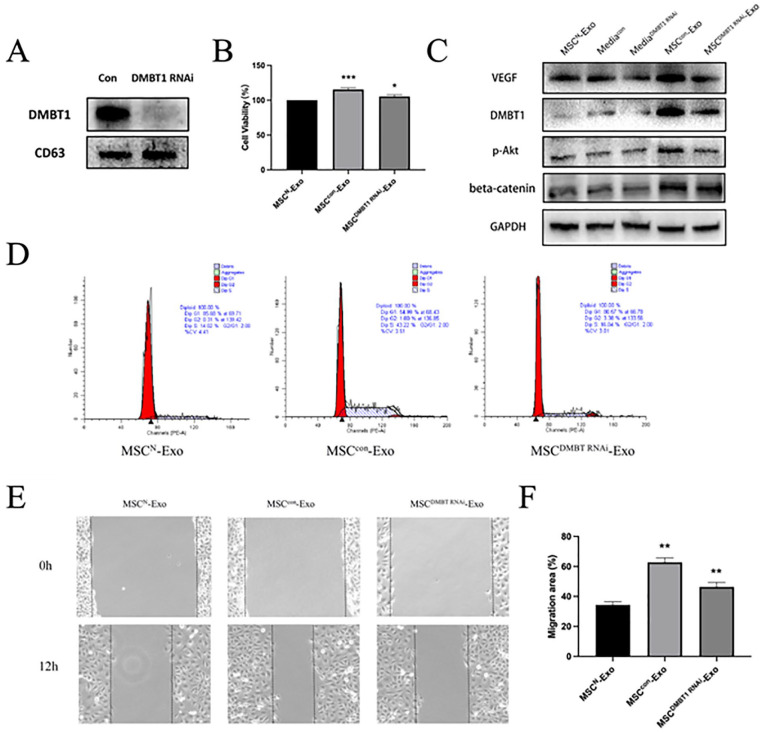
Figure 4.
DMBT1 mediates the pro-angiogenic effects of MSCE-Exos. (A) Western blotting was used to assess DMBT1 knockdown following siRNA transfection (n = 3/group). (B) HUVEC proliferation was assessed via MTT assay following treatment with MSCN-Exos, MSCsCon-Exos, and MSCDMBT1 RNAi-Exos (n = 3/group). *P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001. (C) Western blotting was used to assess DMBT1, p-Akt, β-catenin, and VEGF expression levels in HUVECs in different treatment groups. (D) Cell cycle analyses revealed that HUVECs treated with MSCsCon-Exos exhibited a higher frequency of cells in S phase as compared with HUVECs treated with MSCDMBT1 siRNA-Exos (43.22% vs 16.04%). (E) HUVEC migration following treatment with MSCN-Exos, MSCCon-Exos, or MSCDMBT1 RNAi-Exos was assessed via wound healing assay (n = 3/group). (F) Migration rates were quantified (n = 3/group). **P < 0.05. DMBT1, deleted in malignant brain tumors 1; siRNA, small interfering RNA; HUVEC: human umbilical vein endothelial cell; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PE-A: phycoerythrin absorbance.