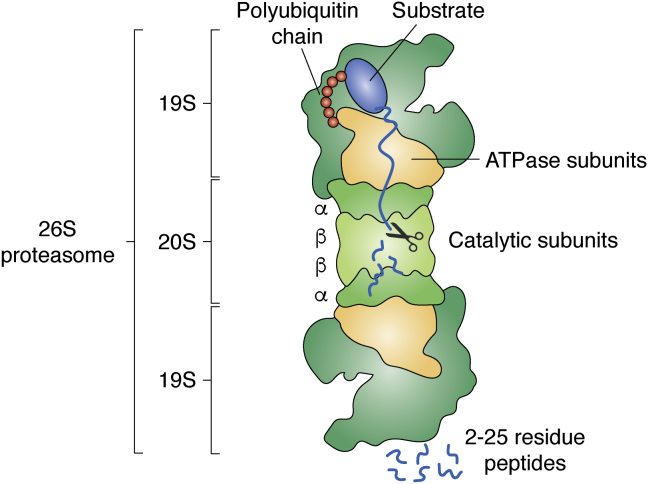
Figure 1.
Structure and function of proteasome holoenzymes. The proteolytic 20S core particle (20S CP) is composed of 14 subunits arranged in four seven-membered subunit rings with α1–7, β1–7, β1–7, α1–7 configuration. The outer α rings contain the gates for substrate entry, while the inner β rings harbor the proteolytic active sites (11, 12). Proteins are degraded into peptides. The base of the 19S regulatory particle (19S RP) recognizes the polyubiquitinated substrate by intrinsic ubiquitin receptor subunits Rpn1, Rpn10, and Rpn13. The RP ATPase ring (Rpt1–6) opens the CP gate and translocates the unfolded polypeptide into the CP cavity, after the polyubiquitin chain has been cleaved off by the DUB Rpn11, a RP lid subunit. The dimensions of the CP are 15 nm in length and 11 nm in diameter; the holoenzyme with RP–CP–RP configuration is ∼45 nm in length (cartoon derived from PDB 4cr2 (115)).