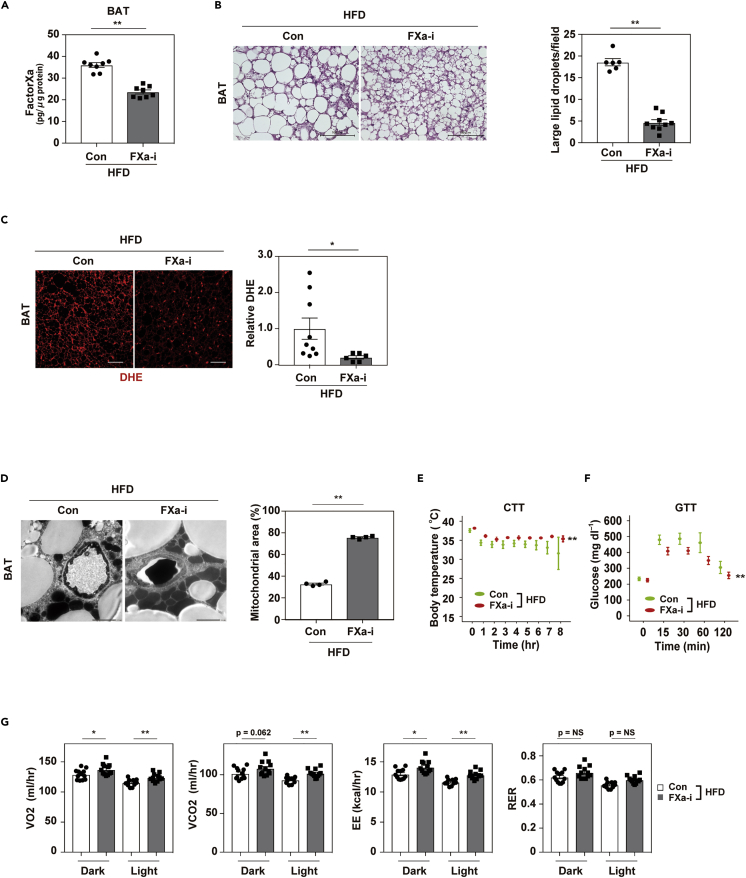
Figure 2.
Inhibition of FactorXa prevents whitening and dysfunction of brown adipose tissue
Mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) from 4 weeks of age with or without the administration of an FXa inhibitor (FXa-i). Physiological studies were performed at age 13 to 19 weeks for FXa-i treatment, and samples were collected at age 18 to 22 weeks.
(A) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay study of Factor Xa in brown adipose tissue (BAT) from mice aged 19-22 weeks fed a high-fat diet (HFD; Con HFD) or HFD + FXa inhibitor (FXa-i HFD; n = 8, 8).
(B) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of BAT from the indicated mice. Scale bar = 100 μm. Right panel indicates the quantification of large lipid droplets in the indicated mice (n = 6, 9). Large lipid droplets were defined as droplets with a surface area >1000 μm2.
(C) Staining with dihydroethidium (DHE) in brown adipose tissue (BAT) from mice fed the HFD (Con HFD) or HFD + FXa-i (FXa-i HFD). Scale bar = 50 μm. Right panels indicate quantification shown as relative dihydroethidium (DHE) level (DHE area of FXa-i HFD/Con HFD, n = 9, 6).
(D) Findings on transmission electron microscopy in the indicated mice (scale bar = 2 μm). Right panels indicate mitochondrial area (%; analyzed as mitochondrial area/[non-capillary and non-lipid area]) in the pericapillary area of respective groups (n = 4, 4).
(E and F) Cold tolerance test (CTT; E, n = 7, 7) or glucose tolerance test (GTT; F, n = 14, 17) in the indicated mice aged 13 weeks for CTT, and 12 weeks for GTT.
(G) Oxygen consumption (VO2), CO2 production (VCO2), energy expenditure (EE), and respiratory exchange ratio (RER) in the indicated groups aged 14-16 weeks (n = 12, 12, 12, 12). Data were analyzed by a 2-tailed Student’s t test (A, B, C, D, G) or 2-way repeated measures ANOVA (E, F). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. Values represent the mean ± SEM NS = not significant. All data are from different biological replicates. See also Figure S2.