Figure 2.
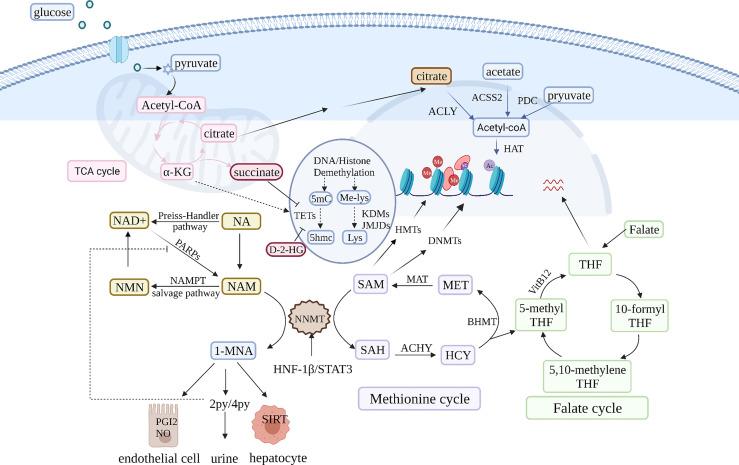
NNMT is pivotal in NAM and SAM metabolism. NNMT uses the universal methyl donor SAM and converts NAM into 1-MNA, which oxidized to 2PY and 4PYand eventually eliminated in the urine. NNMT overexpression leads to a dual drain of NAM and SAM in cancer cells. On one hand, it affects the regeneration of NAD+, a coenzyme of various glucose metabolism enzymes. NNMT over expression decreases NAD+ and contributes to glucose metabolism disorders. The glucose metabolism intermediate α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) is a cofactor of the ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine hydroxylases (TET) and Jumonji C demethylases family (JMJC HDM), which are involved in DNA and histone demethylation, respectively. Furthermore, some glucose metabolism products can enter the nucleus and affect epigenetics. On the other hand, deleting the methyl donor SAM contributes to global hypomethylation and affects the expression of a variety of cancer-associated genes. NNMT also can regulate methyl donor balance by interacting with some enzyme in methionine cycle. In addition to NAM and SAM metabolism, 1-MNA can directly increase Sirt1 protein expression independent of its mRNA level. Sirt1, a regulator of gluconeogenesis and cholesterol synthesis is closely related to NAD+ metabolism. Therefore, NNMT is a pivot in multiple metabolism cycles and influence cancer metabolism from many aspects.