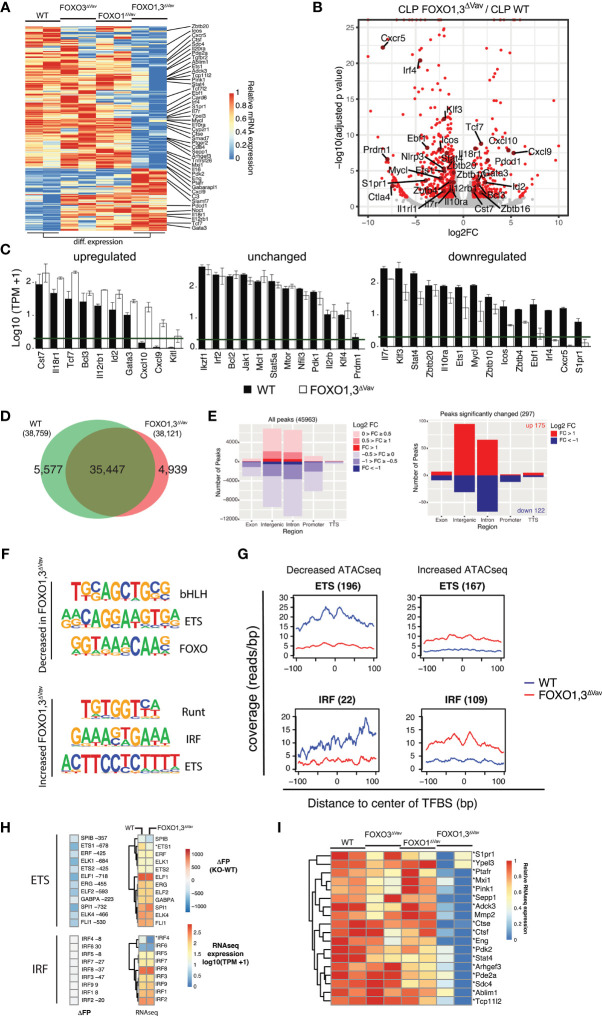
Figure 5.
Removal of FOXO results in NK associated gene regulatory changes at the CLP stage. (A) Heatmap showing row normalized expression of genes with differential expression (adjusted p-value ≤0.01, ≥2-fold change in expression and ≥1 TPM in 2+ samples) between WT and FOXO1,3ΔVav LY6Dneg CLPs. (B) Volcano plot showing log2 fold change and adjusted p-value for the comparison of WT to FOXO1,3ΔVav LY6Dneg CLPs. Red dots indicate genes with >2-fold change in expression and adjusted p-value < 0.05. (C) Bar graphs showing expression (TPM) of select NK associated genes. Genes with adjusted p-value ≤ 0.01, ≥2-fold change in expression and ≥1 TPM in 2+ samples were considered to have the decreased or increased expression. The green line indicates 1 TPM. (D) Venn diagram showing the overlap between ATACseq peaks identified in LY6Dneg CLPs from WT and FOXO1,3ΔVav mice. Only peaks identified in ≥2 replicas each with >30 reads were considered. (E) Annotation of all ATAC-seq peaks identified (left) and peaks with significantly altered chromatin accessibility (adjusted p-value < 0.01 and ≥2-fold change in signal) when comparing LY6Dneg CLPs from WT and FOXO1,3ΔVav mice (right). Number of regions and log2 fold change (FOXO1,3ΔVav/WT) in ATAC-seq signal is indicated. (F) Motifs enriched in differential ATAC-seq peaks. Top three most significantly enriched motifs existing in >10% of regions are displayed. (G) Cut-profiles for differential ATAC-seq peaks with ETS- and IRF-family transcription factor binding sites (TFBS). Number of regions with each TFBS is indicated in parenthesis. (H) Genome-wide difference in the number of footprints (identified in WT and FOXO1,3ΔVav LY6Dneg CLPs) (left) and expression (right) of indicated genes from the ETS- and IRF-families. * indicates significant differences in gene expression between LY6Dneg CLPs from WT and FOXO1,3ΔVav mice. (I) Expression of known ETS1 targets in LY6Dneg CLPs from mice with indicated genotypes.