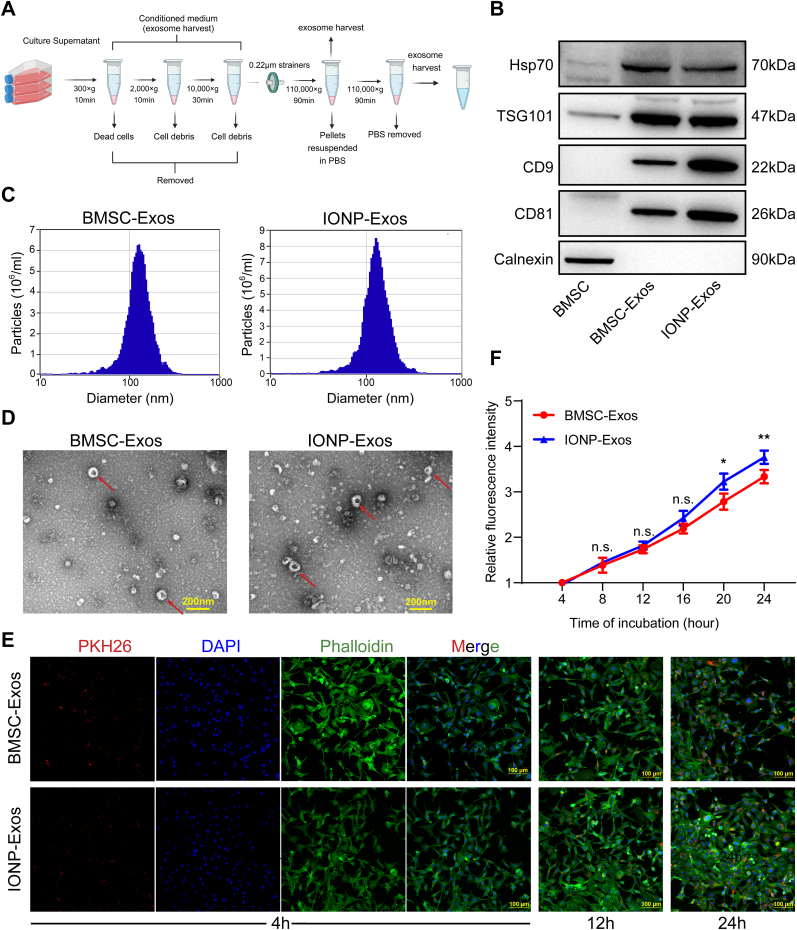
Fig. 2.
Isolation, identification, and comparison of BMSC-Exos and IONP-Exos derived from BMSCs. (A) Schematic representation of the isolation and purification of exosomes by differential ultracentrifugation. All centrifugations were carried out at 4 °C. (B) Western blot analyses of specific surface markers, including Hsp70, CD9, CD81, TSG101, and the negative control calnexin. (C) NTA observation of the diameter distribution of isolated BMSC-Exos and IONP-Exos. (D) Representative image of BMSC-Exos and IONP-Exos observed under a transmission electron microscope. (E) Confocal images showed that the red fluorescence dye PKH26-labeled BMSC-Exos and IONP-Exos were endocytosed by NIH3T3 fibroblasts after 4 h, 12 h, and 24 h of incubation. F-actin was stained with phalloidin (green), and the nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (F) Comparison of the fluorescence intensities of BMSC-Exos and IONP-Exos at different time points. BMSC: bone mesenchymal stem cell; IONP: iron oxide nanoparticle; NTA: nanoparticle tracking analysis. Each assay was performed in triplicate and/or carried out in at least three independent experiments; representative results are shown. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001.