Figure 1.
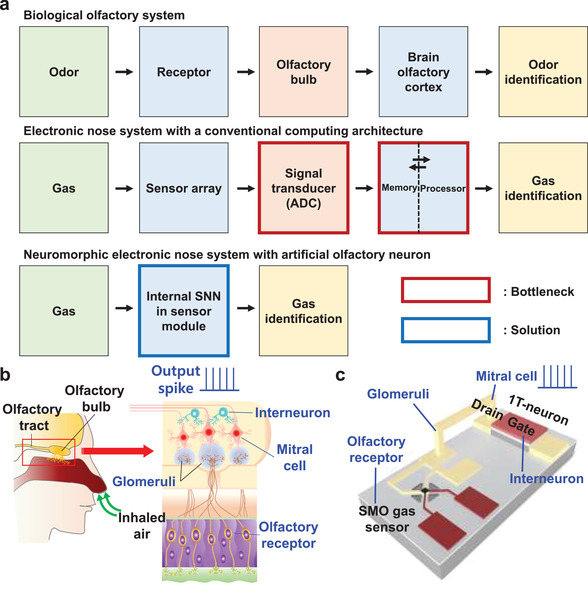
Biological olfactory system and proposed neuromorphic E‐nose system with artificial olfactory neuron. a) Block diagram showing a biological olfactory system, a conventional DNN‐based E‐nose with a conventional processor, and the proposed spiking neural network (SNN) based neuromorphic E‐nose with an artificial olfactory neuron. Limits of hardware cost and energy consumption can be resolved by using an internal SNN in a sensor module. b) A biological olfactory system composed of various olfactory neurons including olfactory receptors, Glomeruli cells, mitral cells, and interneurons in the olfactory bulb. c) A proposed artificial olfactory neuron module composed of a SMO gas sensor and a MOSFET‐based 1T‐neuron. The SMO gas sensor acts as an olfactory receptor that detects odorants. The metal interconnection serves as a Glomeruli that transports signals from the olfactory receptors to the mitral cell. The drain of the 1T‐neuron acts as a mitral cell that receives signals from the olfactory receptors and transmits the spike signals to the olfactory cortex. The gate of the 1T‐neuron serves as an interneuron that inhibits neuronal firing laterally.
