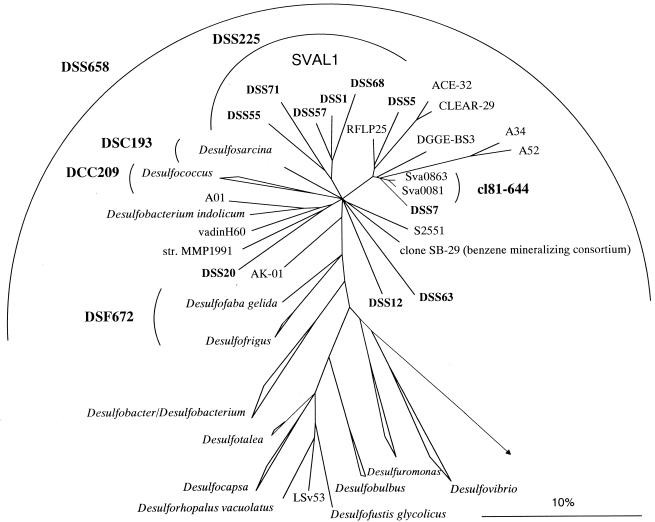
FIG. 4.
Phylogenetic tree showing the affiliations of 16S rDNA clone sequences with selected reference sequences of members of the delta subclass of the Proteobacteria. The tree was calculated by using maximum-likelihood analysis and was corrected with filters which considered only 50% conserved regions of the 16S rRNAs of members of the delta subclass of the Proteobacteria. The DSS clones, as well as clone sequences A01, SB-29, RFLP25, ACE-32, CLEAR-29, A52, A34, and DGGE-BS3, are not full-length sequences (length, 650 to 900 bp) and therefore were added to the existing tree by using a special algorithm included in the ARB software without allowing changes in the tree topology based on almost complete sequences. Different calculations of phylogenetic trees did not result in a stable branching order for some subgroups. Consequently, the phylogenetic affiliations of these subgroups are shown as multifurcations. New cloned 16S rDNA sequences are indicated by boldface type. The group consisting of clone sequences DSS1, DSS5, DSS55, DSS71, and DSS68 was designated SVAL1. Bar = 10% estimated phylogenetic divergence.