Table 1. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm Parameters Obtained from Linearized Dataa.
| model | equation | linear equation | dye | parameters | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pseudo-first order | Qt = Qe (1 – e–k1t) | ln(Qe – Qt) = ln Qe – k1t | RhB | Qe = 15.8 mg g–1 | 0.990 |
| k1 = 0.214 min–1 | |||||
| MO | Qe = 11.6 mg g–1 | 0.856 | |||
| k1 = 0.292 min–1 | |||||
| pseudo-second order | 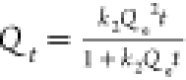 |
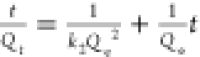 |
RhB | Qe = 19.5 mg g–1 | 0.951 |
| k2 = 0.0125 g mg–1 min–1 | |||||
| MO | Qe = 14.9 mg g–1 | 0.992 | |||
| k2 = 0.0785 mg–1 min–1 | |||||
| Freundlich | Qe = kFCe1/n | 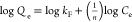 |
RhB | kF = 9.75 | 0.988 |
| n = 1.18 | |||||
| MO | kF = 4.06 | 0.967 | |||
| n = 0.91 |
Qe and Qt are the amount of dye adsorbed per gram of MIL-100(Fe)@PAN (mg g–1) at equilibrium and time t, respectively. k1 and k2 are the pseudo-first-order (min–1) and pseudo-second-order (g mg–1 min–1) rate constants, respectively. Ce is the equilibrium dye concentration in solution (mg L–1). In the Freundlich isotherm model, kF and n are obtained from fitting the experimental results to the model.
