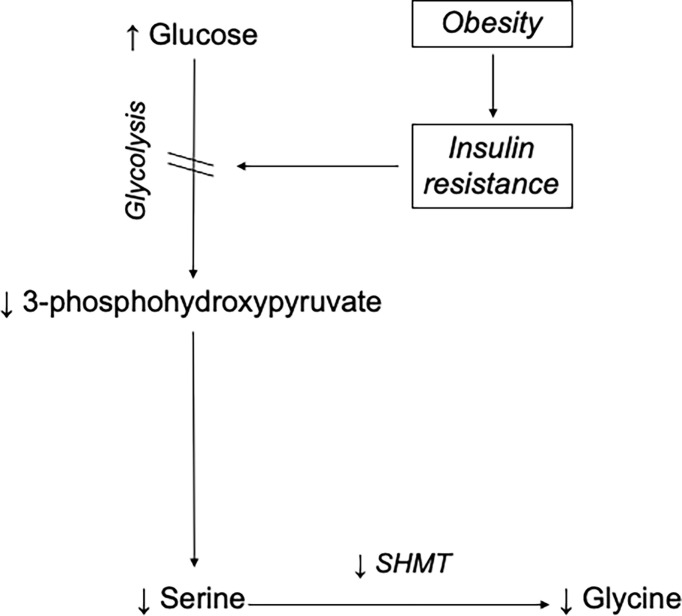
Figure 5.
Mechanism for obesity-associated hypoglycinemia. This model proposes that obesity-induced insulin resistance impairs glucose uptake and results in high plasma glucose concentration. Consequently, glucose flux along the glycolytic pathway decreases, lowering the production of 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate, a major precursor for de novo serine synthesis. Since glycine is mainly synthesized from serine in human, a decreased supply of serine compromises SHMT-mediated de novo glycine synthesis. With time, the overall reduction in glycine production relative to its rate of utilization results in a lowering of its plasma concentration.