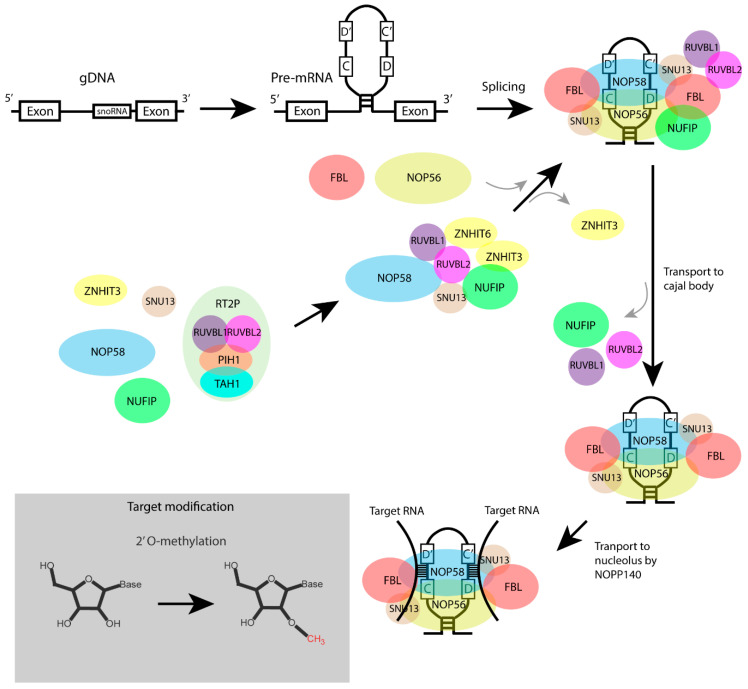
Figure 1.
Biogenesis of C/D box snoRNAs. C/D box snoRNAs are located near the 3′ splice site of the intron. During transcription, C/D box snoRNAs form their characteristic secondary RNA structure. The formation of C/D box snoRNPs requires different assembly factors, including the RUVBL1-RUVBL2-TAH1-PIH1 (R2TP) complex [31,40]. The RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 subunits of the R2TP complex bind, together with nuclear fragile X mental-retardation-interacting protein 1 (NUFIP), zinc finger HIT domain-containing protein 3 (ZNHIT3), and ZNHIT6, the core protein nucleolar protein 58 (NOP58) and small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 13 (SNU13) to form a new protein complex [35]. This newly assembled complex then binds and recruits fibrilarin (FBL), which replaces ZNHIT3 in the complex. The complex binds the C/D box snoRNA sequence during the splicing of the pre-mRNA. RUVBL1, RUVBL2, NUFIP, and ZNHIT6 are released from the complex and the immature snoRNP is translocated to the Cajal body for further maturation before it is translocated to the nucleolus. The mature C/D box snoRNAs are associated with four proteins, SNU13, NOP56, NOP58, and FBL [41,42]. C/D box snoRNA guide the 2′O-methylation of targets rRNAs.