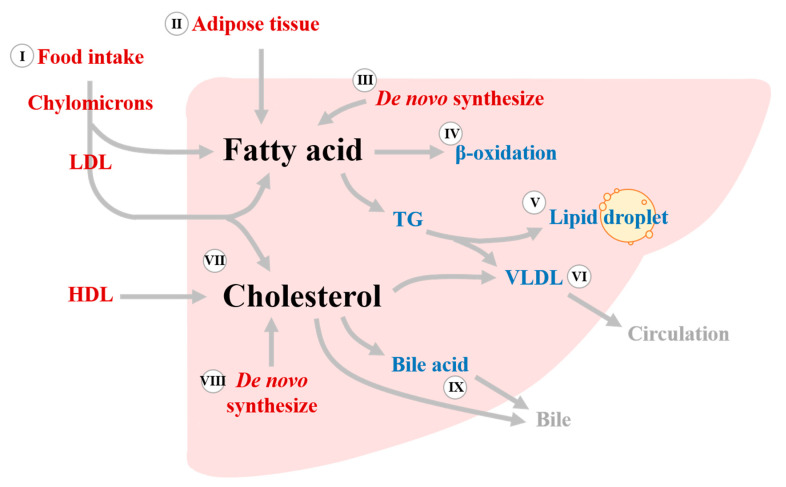
Figure 1.
Lipid metabolism in the liver. The liver is the main site of fatty acid and cholesterol metabolism. Fatty acids come from three main sources: food intake (I), adipose tissue lipolysis (II), and de novo lipogenesis (III). Fatty acids are then used for the production of energy via β-oxidation (IV), synthesis of TGs and storage in lipid droplets (V), or packing into VLDLs and secretion into the circulation (VI). Hepatic cholesterol comes from circulating lipoproteins (LDL and HDL, VII) or de novo synthesis in the liver (VIII). Cholesterol is subsequently used as a component of the plasma membrane of hepatocytes, packaged into VLDLs and released as a cholesterol source for extrahepatic organs (VI), or directly released or converted to bile acid and released into the bile duct (IX). TG, triglyceride; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; and HDL, high-density lipoprotein.