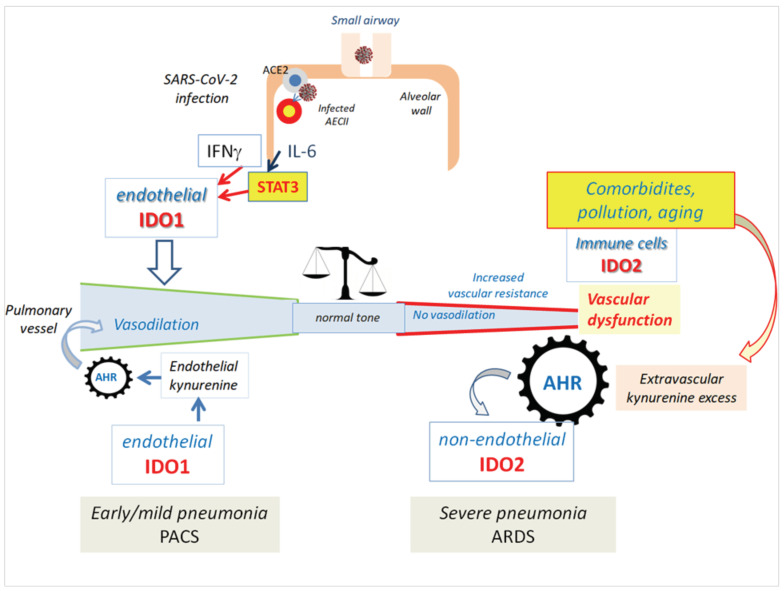
Figure 2.
Hypothetical mechanisms involved in COVID-19 pneumonia, as discussed in this review. After SARS-CoV-2 infection leading to early/mild pneumonia, inflammatory stimuli trigger endothelial IDO1 expression, kynurenine accumulation, and vascular relaxation. This mechanism may persist in post-COVID-19. In severe cases, a loss of vascular IDO1 expression is observed, likely resulting in impairement of vascular-tone control and induction of vascular dysfunction. The occurrence of antecedent abnormal AHR activation (related to old age, comorbidities, and/or pollution) may concur in altering the kynurenine levels and the switch from IDO1 to IDO2.