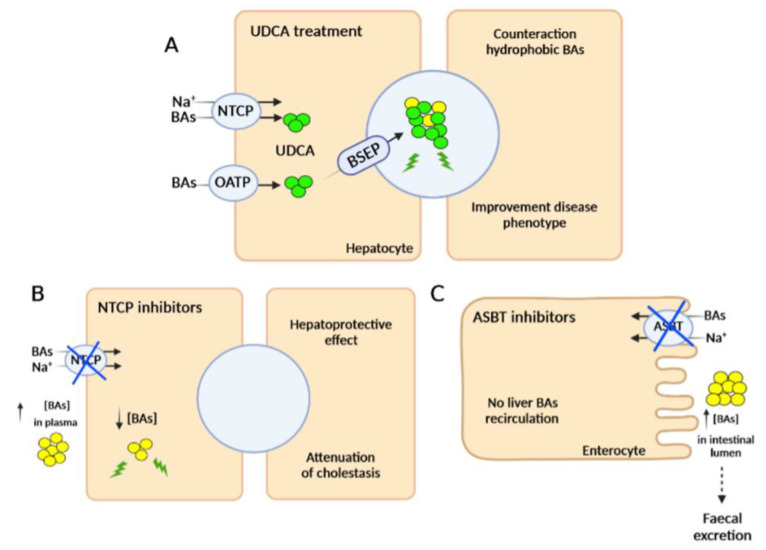
Figure 2.
Pharmacological treatments for cholestatic diseases. (A) Mechanisms of action of UDCA, which favors the presence of hydrophilic BAs over hydrophobic BAs in bile, decreasing the toxic effect of “detergent bile” in cholestatic patients. (B) NTCP transporter inhibitors block the entry of BAs into hepatocytes. (C) ASBT inhibitors prevent the reabsorption of BAs in enterocytes, decreasing their entrance into the enterohepatic recirculation. Inhibitions are indicated with blue crosses. BA, bile acid (yellow circles).