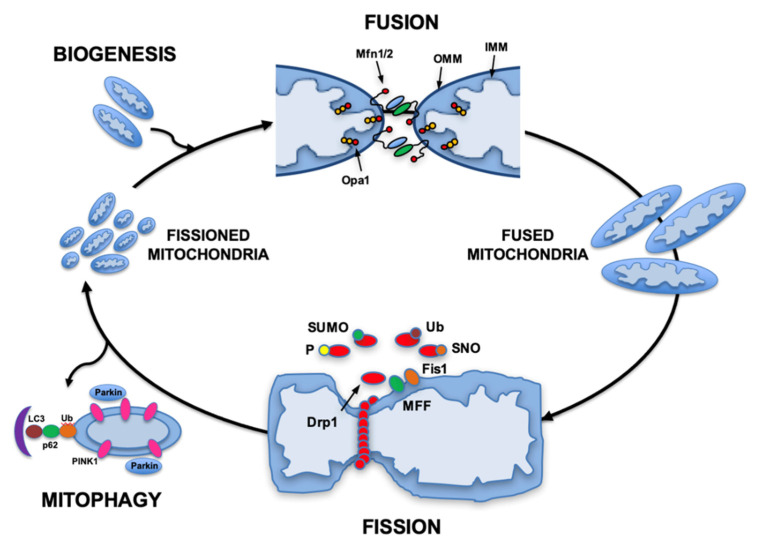
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial dynamics and quality control. The mitochondrial remodeling processes of fission and fusion are both involved in regulating mitochondrial quality control. Mitochondrial fission is regulated by the interaction of mitochondrial proteins (Fis1 or MFF) with the cytosolic protein Drp1, which is translocated from the cytosol to the mitochondria fraction. This process is regulated by several different post-translational modifications (phosphorylation, sumoylation, s-nitrosylation and ubiquitination). During pathological stress, such as induced by ischemia-reperfusions, mitochondria with low membrane potential are marked for mitophagy by accumulation of Pink1, recruitment of Parkin, and are eliminated through autophagy. Mitochondrial fusion is regulated by the interaction of mitochondrial inner (Opa1) and outer membrane proteins (Mfn1/2). Mitochondrial biogenesis is the process that results in synthesis of new mitochondrial proteins and is regulated by the PPARγ coactivator transcriptional coactivators PGC-1α, PGC-1β, and PGC-related PRC. Abbreviations: Drp1, dynamin-related protein 1; Fis1, mitochondrial fission protein 1; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane; LC3, Microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B; MFF, mitochondrial fission factor; MFn, mitofusin; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; Opa1, optic atrophy 1; PGC-1, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1; PINK1, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1; PPARγ, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PRC, PGC-1-related coactivator; SNO, S-nitrosylated; SUMO, small ubiquitin-like modifier protein; Ub, ubiquitin. (From Gottlieb and Bernstein [3]. Based in part on Archer et al. [4]).