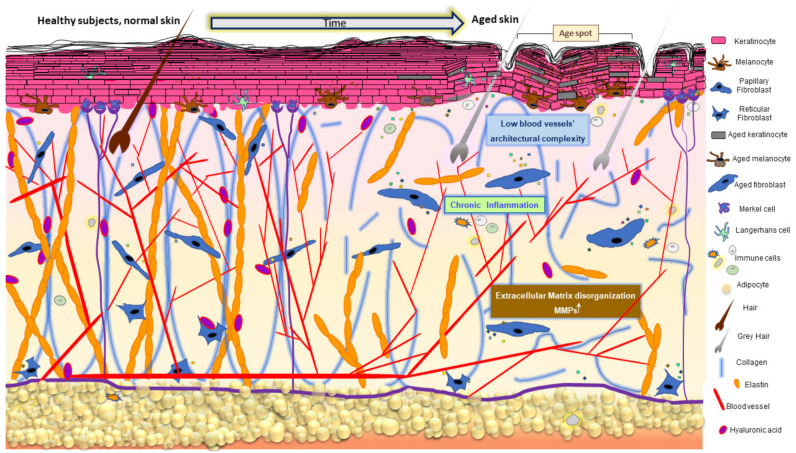
Figure 2.
Age-related changes in the skin. Skin aging results in cumulative detrimental effects characterized by abnormal ECM organization, pigmentary changes, loss of subcutaneous fat, hair greying, minored hair density, decreased sebaceous gland function, and low-grade chronic inflammation. Cellular and molecular events reviewed in the text describe the impact of oxidative disequilibrium on these time-dependent and/or extrinsically accelerated tissue transformations.