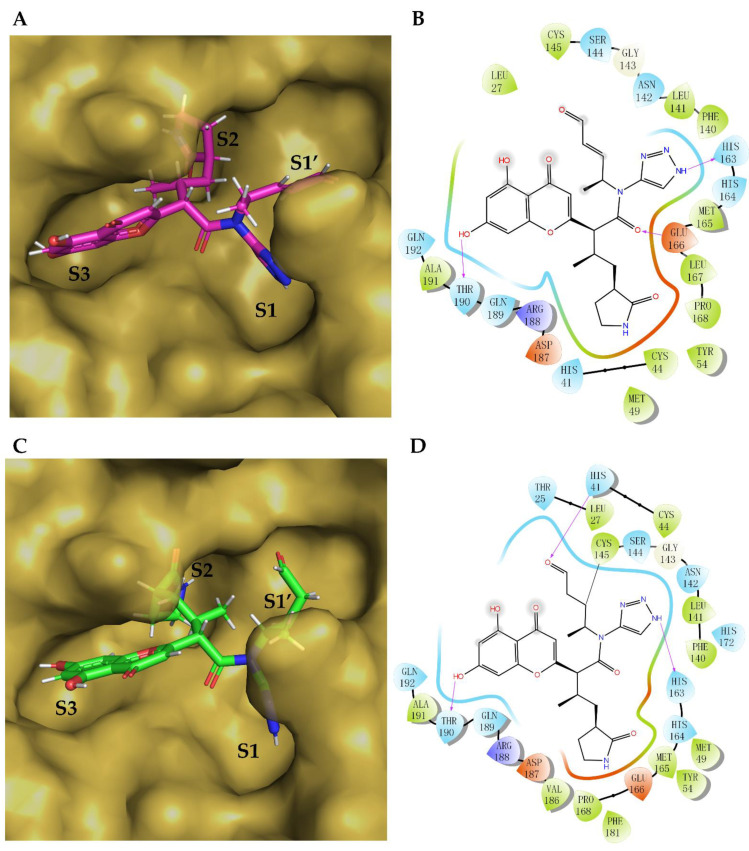
Figure 3.
Lead compound #46 generated by AI. (A) Non-covalent docking model of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro (brown surface) with the bound lead compound #46 (magenta sticks). The triazole ring binds to the S1 subsite of the active catalytic center, the covalent fragment of the α, β-unsaturated aldehyde binds to the S1′ subsite, the β-lactam ring binds to the S2 subsite, and 5,7-dihydroxy chromone binds to the S3 subsite. (B) Two-dimensional (2D) view of the non-bonding interactions of lead compound #46 in complex with 3CL protease based on non-covalent docking. The triazole ring, ketoamide group, and phenolic hydroxyl group form hydrogen bonds (H-bonds) with His163, Glu166, and Thr190, respectively. (C) Covalent docking model of compound #46 (green sticks) with 3CL protease (brown surface), similar to the non-covalent docking model. (D) Two-dimensional view of ligand interactions between compound #46 and protease under covalent docking. The triazole ring forms an H-bond with His163. The α, β-unsaturated aldehyde forms a covalent bond with Cys145, i.e., the key residue in the catalytic center of the protease, resulting in covalent inhibition. The aldehyde carbonyl group forms an H-bond with His41. The hydroxyl group of chromone at position 7 forms an H-bond with Thr190.