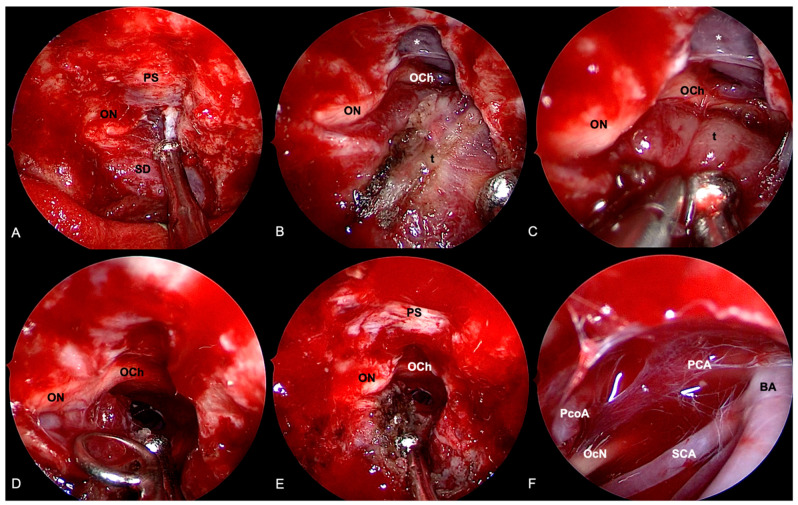
Figure 8.
Extended endoscopic endonasal approach for removal of right cavernous sinus meningioma. (A) Bone removal encompasses the opening of the mesial aspect of the right optic foramen. (B) Sellar dura and planum sphenoidale are exposed. The tumor is coagulated, and the removal proceeds by means of intra and extracapsular dissection. A cleavage plane is found between the lesion and the optic chiasm (C) and nerve (D). (E) After optic nerve and chiasm decompression, the tumor is not followed inside the cavernous sinus. (F) Exploration of the interpeduncular cistern through a subchiasmatic window: Basilar artery (BA) and right posterior cerebral artery (PCA), posterior communicating artery (PcoA), and oculomotor nerve (OcN) are identified. Tumor (t); sellar dura (SD); planum sphenoidale (PS); optic nerve (ON); optic chiasm (OCh); oculomotor nerve (OcN); posterior communicating artery (PcoA); posterior cerebral artery (PCA); basilar artery (BA); superior cerebellar artery (SCA); lamina terminalis cistern (*).