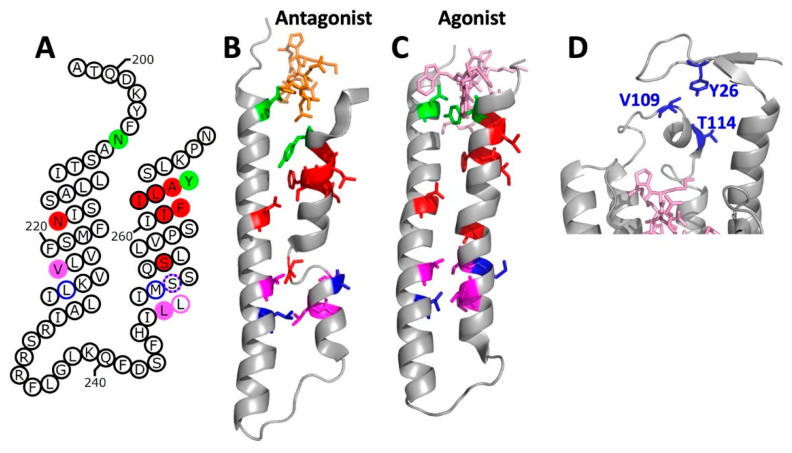
Figure 5.
Locations of confirmed and putative disulfide crosslinks involving TM5 and TM6 (transmembrane segments 5 and 6). (A) Interactions identified by Lee et al. [57] are shown in green, interactions identified by Dube et al. [58] are shown in magenta and blue, and interactions shown by Taslimi et al. [59] are shown in red. In each case, disulfides confirmed by peptide mapping are indicated by colored fills. Putative interactions identified based on constitutive activation that was dependent on the presence of cysteine at paired sites are indicated by a colored circle around the indicated residue. (B) Locations of putative crosslinks mapped onto the three-dimensional structures of TM5 and TM6 in the antagonist-bound receptor structure (PDB Code: 7QA8). Colors are as shown in (panel A), but with no distinction between demonstrated functional and biochemically-confirmed interactions. Bound antagonist is shown in stick representation in orange. (C) Same as for (panel B), but mapped onto TM5 and TM6 of the agonist-bound receptor G protein complex (PDB code: 7AD3). Note that the cysteine replacement at residue S251 shows functional interactions with cysteines at the positions of either V223 or L226. This is indicated by alternating colored dashed circles in (panel A), but the residue is only colored as magenta in (panels B and C). Bound α-factor is shown in stick representation in pink. (D) Locations of putative crosslinks between cysteines substituted for Y26 in the N-terminal tail of Ste2p and for V109 and T114 in EC1. Relevant residues are shown in blue as stick representations.