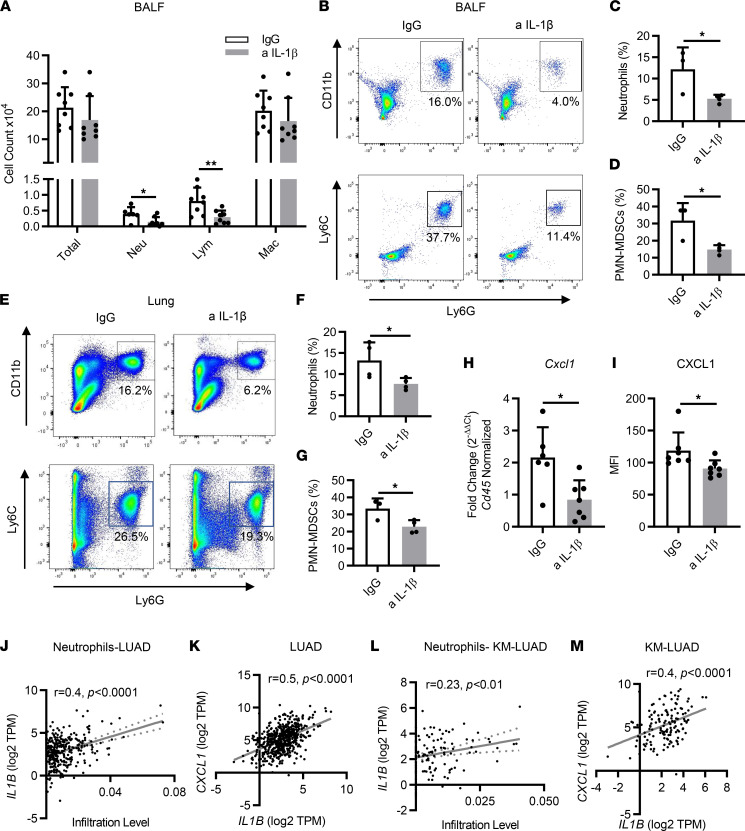
Figure 2. Immunopreventive blockade of IL-1β decreases protumor immune cells.
(A) Total inflammatory cell and lineage-specific leukocyte numbers from BALFs of 14-week-old CC-LR mice treated with IgG or anti–IL-1β Ab (n = 8). (B–G) Representative flow cytometry analysis and quantification of neutrophils (CD11b+Ly6G+) and PMN-MDSCs (CD11b+Ly6CloLy6G+) in (B–D) BALFs and (E–G) whole lungs (n = 3–4). (H) Relative mRNA expression of Cxcl1 in the whole lung normalized to Cd45 expression (n = 6–7). (I) MFI of CXCL1 measured by multiplex ELISA in IgG or anti–IL-1β Ab–treated mice (n = 7). (J) Correlation between IL1B expression and infiltration of neutrophils in LUAD (n = 533). (K) Correlation between IL1B expression and CXCL1 expression in LUAD (n = 535). (L) Correlation between IL1B expression and infiltration level of neutrophils in KM-LUAD (n = 138). (M) Correlation between IL1B expression and CXCL1 expression in KM- LUAD (n = 139). Data represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.5 by unpaired t test. a IL-1β, anti–IL-1β; Lym, lymphocytes; Mac, macrophages; Neu, neutrophils; TPM, transcript count per million.