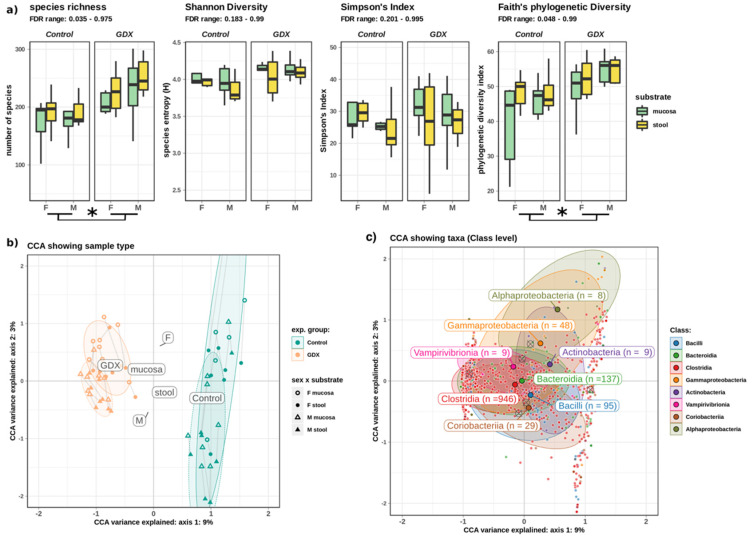
Figure 3.
Microbial diversity. (a) Alpha diversity (richness and phylogenetic diversity) was increased following gonadectomy, but it did not differ significantly between sexes or substrates. (b) Beta diversity (CCA of sample composition), showing the significant influence of both experimental group and sex, as illustrated by the strong separation of labels (centroids) for F and M controls, which is resolved by GDX. The substrate had a non-significant effect, as illustrated by the co-location of labels near the origin. (c) The same CCA showed taxa as points closest to samples where they were most abundant (e.g., Gammaproteobacteria tended to be more abundant in control-F). Crossed circles indicate location of group centroids. Paired samples are joined by a line. Asterisk (*) denotes significant difference at FDR < 0.05, whereas a horizontal bracket indicates that the difference is between the GDX and control overall. Abbreviations: F: female; M: male; GDX: gonadectomy; CCA: constrained correspondence analysis.