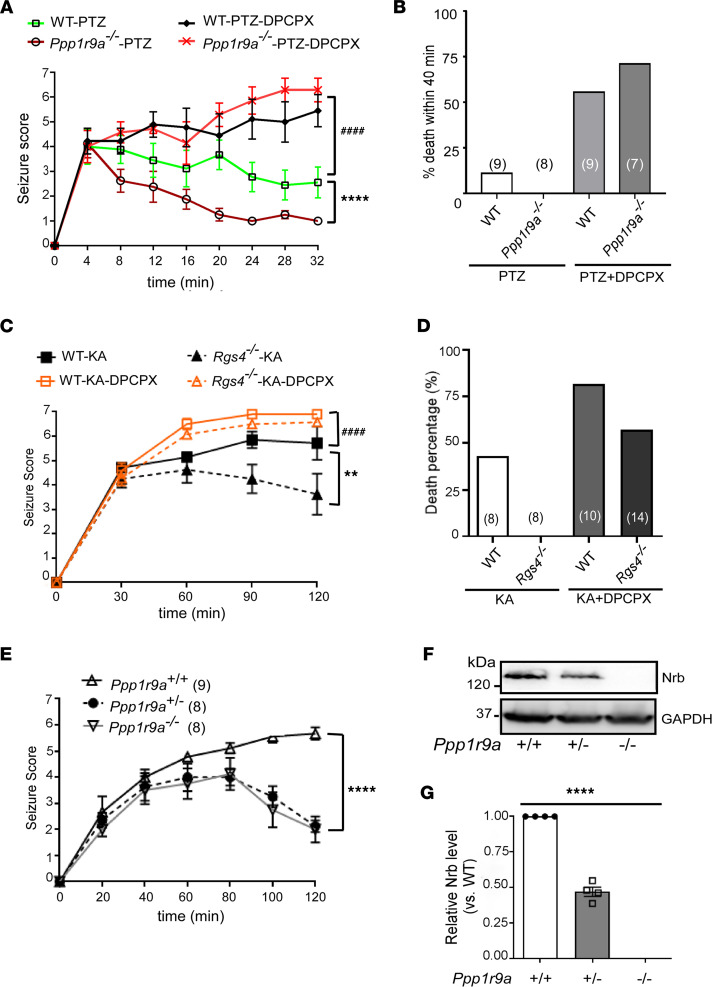
Figure 1. The A1R-mediated anticonvulsant effect is regulated by neurabin and RGS4 and is particularly sensitive to the change in neurabin levels.
(A) Neurabin deficiency (Ppp1r9a–/–) attenuates seizure severity in response to PTZ. Seizure activity over time following PTZ injection was scored. n = 8–9/group. ****P < 0.0001, Ppp1r9a–/– versus WT mice by 2-way ANOVA. ####P < 0.0001, WT mice treated with PTZ alone versus PTZ plus DPCPX by 2-way ANOVA. (B) PTZ-induced lethality within 40 minutes following injection is recorded in mice examined in A. The number of mice in each group is indicated in parentheses. (C) Seizure severity in response to kainate is measured in the Rgs4–/– mouse line and its corresponding WT line. n = 8–14/group. **P < 0.01, Rgs4–/– versus WT mice. ####P < 0.0001, WT mice treated with kainate alone versus kainate plus DPCPX by 2-way ANOVA. (D) Kainate-induced lethality is recorded in mice examined in C. Data are expressed as percentage of death in WT and Rgs4–/– mice caused by administration of kainate alone or with DPCPX. The number of mice in each group is indicated in parentheses. (E) A1R-mediated anticonvulsant effects are enhanced in mice with reduced neurabin expression. Seizure severity in response to kainate is attenuated in both Ppp1r9a+/– and Ppp1r9a–/– mice. The number of mice in each group is indicated in parentheses. ****P < 0.0001, Ppp1r9a+/– versus Ppp1r9a+/+ mice by 2-way ANOVA. (F and G) Expression of neurabin in brain lysates of Ppp1r9a+/+, Ppp1r9a+/–, and Ppp1r9a–/– mice. (F) Representative Western blots. (G) Quantitation of expression levels of neurabin in the brain of mice with indicated genotypes. ****P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA. n = 4/group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. See complete unedited blots in the supplemental material; supplemental material available online with this article; https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.155002DS1.