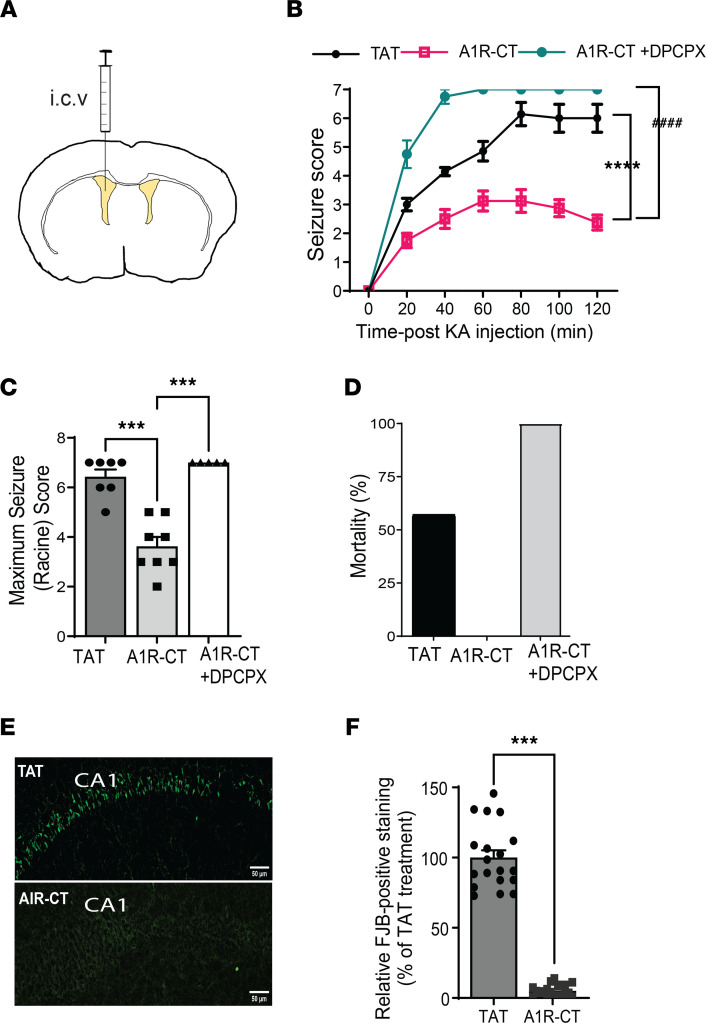
Figure 5. The A1R-CT peptide displays robust anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects in an A1R dependent manner.
(A) A schematic diagram indicates the TAT-fused A1R-CT peptide or TAT control peptide infused into the left ventricle 30 minutes prior to kainate injection. (B) Seizure severity in response to kainate is measured in mice with indicated treatment. ****P < 0.0001, A1R-CT versus TAT; ####P < 0.0001, A1R-CT versus A1R-CT+DPCPX, by 2-way ANOVA. n = 7 for TAT and A1R-CT+DPCPX; n = 8 for A1R-CT. (C) Quantitation of maximum seizure scores in mice with indicated treatment. ***P < 0.01 by 1-way ANOVA Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Kainate-induced lethality is recorded in mice examined in B. Data are expressed as percentage of death. (E) Representative images of cell death in the hippocampal CA1 region as revealed by Fluoro-Jade B (FJB) staining. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) Quantitation of the CA1 neurons with positive FJB staining. Data are expressed as the percentage of the level in TAT-treated mice (which is set as 100%). ***P < 0.001 by paired 2-tailed Student’s t test. n = 19 slices from 3 mice for TAT and n = 19 slices from 3 mice for A1R-CT. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.