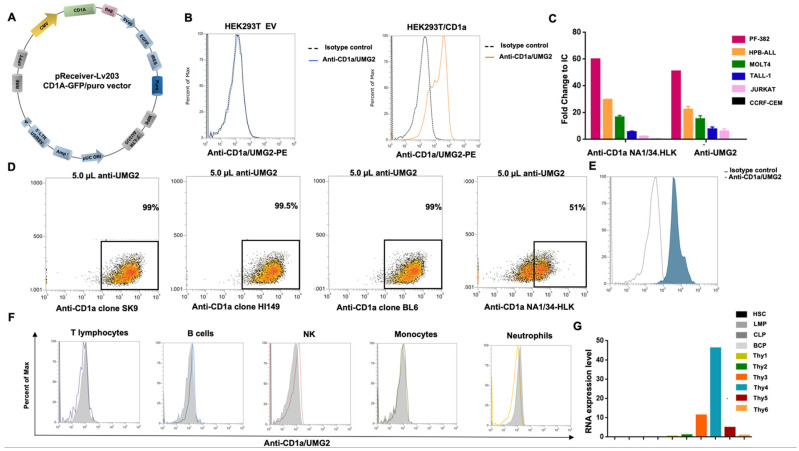
Figure 1.
UMG2 mAb binding reactivity. (A) Graphical representation of CD1a/GFP vector map. (B) UMG2 reactivity on HEK293T cell line transfected with empty vector (left) or CD1a-expressing plasmids (right). (C) Reactivity of anti CD1a clone NA1/34-HLK and anti-UMG2 on T-ALL cell lines. (D) Competitive binding assay between unconjugated anti-UMG2 and commercially available anti-CD1a fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies (Bl6, SK9, HI14, and NA1/34-HLK) on HPB-ALL cell line. Only NA1/34-HLK anti-CD1a commercial clones partially compete with anti-UMG2. (E) Representative FACS data of UMG2 binding reactivity on primary T-ALL cells. (F) UMG2 binding on peripheral blood cells from healthy donors. (G) CD1a RNA expression level on human bone marrow and thymic progenitor cells.